a
b
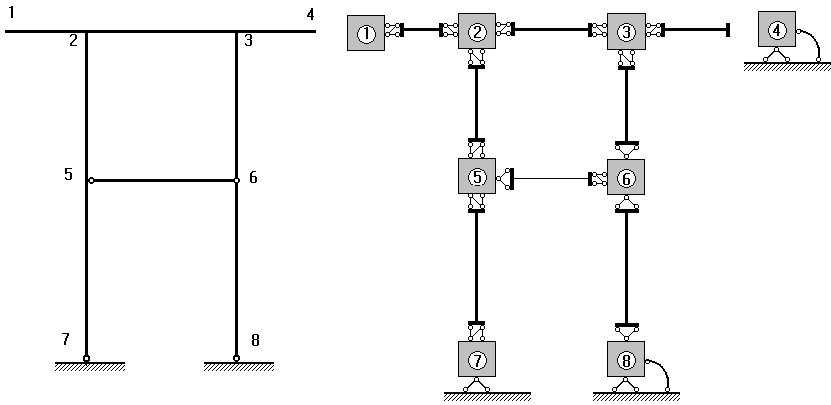
Figure 1. Depiction of a design model: (a) traditional; (b) detailed.
Nodes (located in the end sections of bars) of elements joined to the nodes of the system can be located at some distance from the center of the model node, i.e., a junction eccentricity may take place. We will assume that in all element types where this eccentricity is allowed, the node (end section) of an element will be connected to the center of the model node by a rigid insert, and this insert will be a part of the finite element.
Obviously, the presence of the said rigid insert will make the displacement of the element end section unequal to that of the model node (the former depends also on the nodal rotations), while the rotation angles of the node and of the end section will be equal.
The difference between the displacements (rotation angles) of a node and the element end section connected to the model node may be also caused by the peculiarities of the junction design. Assuming that an element can be connected by its nodes to the centers of the model nodes through six constraints, each one restraining one of six possible mutual displacements, we can also imagine the absence of any of these six constraints. The absence of one angular constraint corresponds to a cylindrical hinge; the absence of all three mutual angular constraints – to a spherical hinge; the absence of a linear constraint – to a “slider”, etc. To be brief, we will further refer to all cases of this kind as “hinges”, though it is not very accurate. It should be noted that the use of various junctions between the elements and the nodes, as well as constraints imposed on the nodal displacements, enables to diversify our design models. This fact is illustrated by Fig. 1. We recommend you to compare equal though represented in different ways pairs of nodes 1 and 4, or 7 and 8.
|
|
a |
b |
Figure 1. Depiction of a design model: (a) traditional; (b) detailed. |
|
It should be noted that the incomplete equivalence between the element and the model nodal displacements, as well as the eccentric junction, is allowable not for every element type; one should refer to finite element definitions to find out whether those are possible. Limitations, if there are any, can be circumvented using artificial tricks (by introducing additional nodes, very compliant constraining elements etc.).