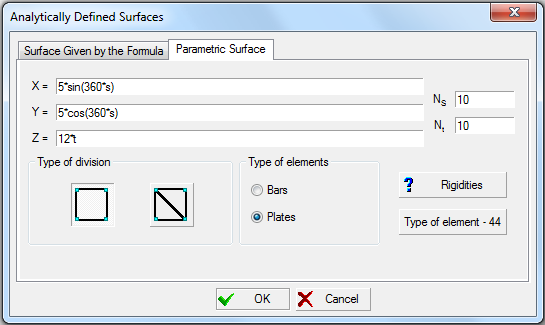
In addition to the operation of creating analytic surfaces (by the specified formula) the software also enables to generate parametric surfaces. Initial data for this operation are specified in the Parametric Surface tab of the Analytically Defined Surfaces dialog box (Fig. 1).

Figure 1. The Parametric Surface tab of the Analytically Defined Surfaces dialog box
The following relationships are considered x = f(s,t), y = f(s,t), z = f(s,t). It is assumed that each variable s and t changes in the interval [0, 1], and the variable s successively takes the values 0, 1/Ns, 2/Ns, … 1, and the variable t — respectively 0, 1/Nt, 2/Nt, … 1, where Ns and Nt — number of steps of tabulation of the respective variables.
For example, formulas describing the surface of a cylinder with a radius 5 and height 12, will be as follows:
x = 5 sinα;
y = 5 cosα;
z = 12 h
and must be input in the respective text fields of the Parametric Surface tab as follows:
x = 5*sin(360*s);
y = 5*cos(360*s);
z = 12*t.
This tab also enables to specify the values of Ns and Nt., select finite elements (bars or plates) and the type of division of the surface. If the type of finite elements is different from the default one, it can be changed with the help of the respective operation which can be invoked by clicking the Type of element button. Type 5 is assigned to bar elements by default, and types 44 (4-node) and 42 (3-node) — for shells depending on the selected shape of division. The Rigidities button invokes an operation of specifying the stiffness properties of elements.
Note: if the formula involves trigonometric or inverse trigonometric functions, it should be taken into account that their arguments (or calculated values) must be in degrees.