Strength of normal section (bending). Nonlinear deformation model
Objective: Check the strength of the section by deformation model using a three-line axial compression diagram of concrete
Task: Determine the relative strains in the compressed concrete and in the tensile reinforcement
References: E.N. Kodysh, N.N. Trekin, I.K. Nikitin, K.E. Sosedov. Practical methods and examples of calculation of reinforced concrete structures from heavy concrete according to SP 63.1330. - Monograph. M.: Publishing and printing enterprise of LLC “Bumazhnik”, 2017. - 496 с. (Example 13, pp. 181-187)
Initial data file:
ARBAT program section – Check, mode – Strength of RC Sections
Example-13-SP.SAV
отчет – Arbat 13-SP-dm.doc
Compliance with the codes: СП 63.13330.2012.
Initial data:
|
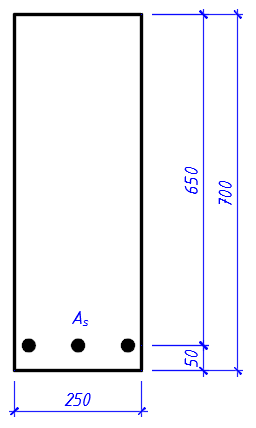
b×h = 250×700 mm |
Cross-section sizes |
|
а1= 34 mm |
Distance from the edge of the lower reinforcement to the lower edge of the cross-section (protective layer) |
|
As1 = 2413 mm2 (3Ø32) |
Area of the lower reinforcement |
|
М= 100 кНm |
Bending moment |
|
Concrete class |
В25 |
Initial data in ARBAT:
Importance factor γn = 1
Importance factor (Serviceability limit state) 1
Member length 1 m
Effective length factor in the XoY plane 1
Effective length factor in the XoZ plane 1
Random eccentricity along Z according to SP 63.13330.2012
Random eccentricity along Y according to SP 63.13330.2012
Structure is statically determinate
Limit slenderness - 200
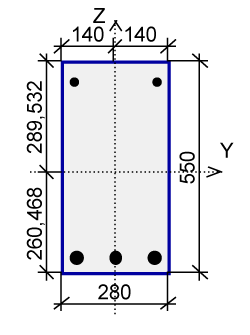
Section
|
b = 250 mm h = 700 mm a1 = 34 mm a2 = 20 mm
|
S1 - 3Ø32 |
|---|
|
Reinforcement |
Class |
Additional service factor |
|---|---|---|
|
Longitudinal |
A400 |
1 |
|
Transverse |
A240 |
1 |
Concrete
Concrete type: Heavy-weight
Concrete class: B25
|
Additional parameters |
||
|---|---|---|
|
γb1 |
allowance for the sustained loads |
1 |
|
γb2 |
allowance for the failure behavior |
1 |
|
γb3 |
allowance for the vertical position during concreting |
1 |
|
γb5 |
allowance for the freezing/thawing and negative temperatures |
1 |
Humidity of environment air - 40-75%
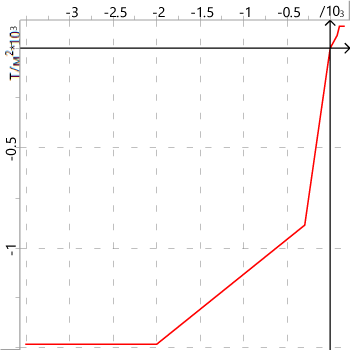
Compressed concrete state diagram
Results of analysis by load case combinations
|
|
N |
My |
Qz |
Mz |
Qy |
T |
Safety factor for load |
Factor for sustained load |
Short-term |
Seismicity |
Special |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
kN |
kN*m |
kN |
kN*m |
kN |
kN*m |
||||||
|
1 |
0 |
100 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
Checked according to SP |
Check |
Utilization Factor |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Ultimate moment strength of the section |
0,22379 |
|
Sec. 8.1.20-8.1.30 |
Strains in compressed concrete |
0,05734 |
|
Sec 8.1.20-8.1.30 |
Strains in the tensile reinforcement |
0,01447 |
|
Sec. 8.2.15, 8.2.16, 8.2.6 |
Crack opening width (short-term) |
0,46449 |
|
Sec. 8.2.6, 8.2.15, 8.2.16 |
Crack opening width (long-term) |
0,30966 |
Comparison of solutions
|
Check |
Strains in compressed concrete |
|
Example |
0,00019/0,0035=0,054 |
|
ARBAT |
0,05734 |
|
Deviation, % |
5,5 % |
|
Check |
Strains in the tensile reinforcement |
|
Example |
0,00036/0,025=0,0144 |
|
ARBAT |
0,01447 |
|
Deviation, % |
0,5 % |
Note: there are typos in the example, once corrected, the strain deviation in compressed concrete will be less than 1%.