Tee Slab Deflection Analysis
Objective: Check of the slab deflection analysis
Task: Verify the correctness of the deflection calculation
References: Guide on designing of concrete and reinforced concrete structures made of heavy-weight or lightweight concrete (no prestressing) (to SNiP 2.03.01-84), 1989, p. 140-141.
Initial data file:
Example 59.SAV
report – Arbat 59.doc.
Compliance with the codes: SNiP 2.03.01-84*.
Initial data:
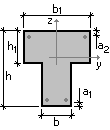
| l = 5,7 m | Slab span |
| b×h = 80×300 mm | Slab section sizes |
| а = 31 mm | Distance from the center of gravity of the reinforcement to the compressed edge of the section |
| As = 380 mm2 (1Ø22) | Cross-sectional area of reinforcement |
| ql = 8,75 kN/m | Permanent and long-term distributed load |
|
Concrete class |
В25, D1600 |
ARBAT initial data:
Importance factor γn = 1
Structure:
Section:
|
b = 80 mm |
|
|
Reinforcement |
Class |
Service factor |
|
Longitudinal |
A-II |
1 |
|
Transverse |
A-I |
1 |
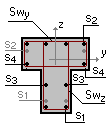
Specified reinforcement:
|
Span |
Segment |
Length (m) |
Reinforcement |
Section |
|
span 1 |
1 |
5.7 |
S1 - 1Ø22
|
|
Concrete:
Concrete type: Lightweight
Concrete class: B25
Grade by average density: D1600
Aggregate: Artificial dense
Density of concrete 1.6 T/m3
Hardening conditions: In steam-curing chambers
Hardening factor 1
|
Service factor for concrete |
||
|---|---|---|
|
γb2 |
allowance for the sustained loads |
1 |
|
|
resulting factor without γb2 |
1 |
Conditions of operation:
Mode of concrete humidity - Natural humidity
Humidity of environmental air - 40-75%
Comparison of solutions:
|
Check |
maximum deflection |
|
Guide |
23,2 mm |
|
ARBAT |
22,905 mm |
|
Deviation, % |
1,3 % |
Comment. The difference in the results is due to the fact that approximate empirical formulas are used in the Guide.