Geometric Properties of an Ellipse
Aim: To check the accuracy of the geometric properties calculation for a solid elliptical cross-section of a rod.
Name of a file with the initial data: Ellipse_Solid.cns
Formulation: Check the accuracy of the geometric properties calculation for a solid elliptical cross-section of a rod.
References: Demidov S. P., Theory of Elasticity, M., Vysshaya Shkola, 1979.
Lurie A. I., Theory of Elasticity, M., Nauka, 1970.
Initial data:
| ν = 0.30 | - Poisson’s ratio; |
| a = 50 cm | - length of the semi-major axis of the elliptical cross-section (along Y axis); |
| b = 30 cm | - length of the semi-minor axis of the elliptical cross-section (along Z axis). |
Design model: The design model is created by triangulation (the number of triangles ≈ 3000) on the basis of a model of the external contour imported from the AutoCad graphic editor. The model of an external contour is a polygon inscribed in an ellipse with given properties and built in polar coordinates with an angle step of 3°. The number of vertices of a polygon in a model is 120.
Results Obtained in Consul
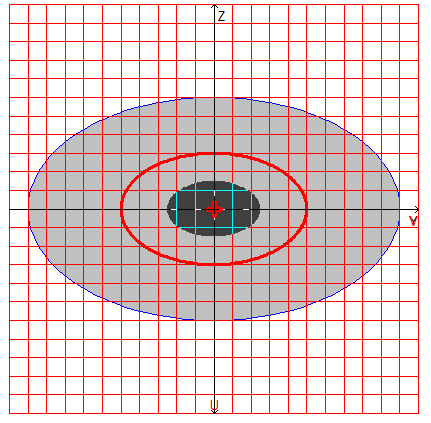
Design model, coordinate and principal axes, center of mass, ellipse of inertia, core of the section
Comparison of results:
|
Parameter |
Theory |
CONSUL |
Deviation, % |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Cross-sectional area, A cm2 |
4712.389 |
4709.319 |
0.07 |
|
Conventional shear area along the principal U-axis, Av,y cm2 |
3724.143 |
3702.975 |
0.57 |
|
Conventional shear area along the principal V-axis, Av,z cm2 |
4147.170 |
4161.672 |
0.35 |
|
Angle of the principal axes of inertia α rad |
1.5708 |
1.5708 |
0.00 |
|
Moment of inertia about the centroidal Y1 axis parallel to the coordinate Y axis, Iy cm4 |
1060287.521 |
1059491.143 |
0.08 |
|
Moment of inertia about the centroidal Z1 axis parallel to the coordinate Z axis, Iz cm4 |
2945243.113 |
2939784.432 |
0.19 |
|
Torsional moment of inertia, It cm4 |
3118492.708 |
3064969.367 |
1.72 |
|
Sectorial moment of inertia, Iw cm6 |
97835065.337 |
95561910.155 |
2.32 |
|
Radius of gyration about Y1 axis, iy cm |
15.000 |
14.980 |
0.13 |
|
Radius of gyration about Z1 axis, iz cm |
25.000 |
24.991 |
0.04 |
|
Maximum section modulus about U-axis, Wu+ cm3 |
58904.862 |
58795.689 |
0.19 |
|
Minimum section modulus about U-axis, Wu‒ cm3 |
58904.862 |
58795.689 |
0.19 |
|
Maximum section modulus about V-axis, Wv+ cm3 |
35342.917 |
35316.371 |
0.08 |
|
Minimum section modulus about V-axis, Wv‒ cm3 |
35342.917 |
35316.371 |
0.08 |
|
Plastic section modulus about U-axis, Wpl,u cm3 |
100000.000 |
99796.050 |
0.20 |
|
Plastic section modulus about V-axis, Wpl,v cm3 |
60000.000 |
59820.326 |
0.30 |
|
Maximum moment of inertia, Iu cm4 |
2945243.113 |
2939784.432 |
0.19 |
|
Minimum moment of inertia, Iv cm4 |
1060287.521 |
1059491.143 |
0.08 |
|
Maximum radius of gyration, iu cm |
25.000 |
24.985 |
0.06 |
|
Minimum radius of gyration, iv cm |
15.000 |
14.999 |
0.01 |
|
Core size along positive Y(U)-axis, a u+ cm |
7.500 |
7.494 |
0.08 |
|
Core size along negative Y(U)-axis, a u‒ cm |
7.500 |
7.480 |
0.27 |
|
Core size along positive Z(V)-axis, a v+ cm |
12.500 |
12.491 |
0.07 |
|
Core size along negative Z(V)-axis, a v‒ cm |
12.500 |
12.491 |
0.07 |
|
Y-coordinate of the center of mass, ym cm |
0.000 |
0.000 |
— |
|
Z-coordinate of the center of mass, zm cm |
0.000 |
0.000 |
— |
|
Y-coordinate of the shear center, yb cm |
0.000 |
0.013 |
— |
|
Z-coordinate of the shear center, zb cm |
0.000 |
0.040 |
— |
|
Perimeter, P cm |
255.180 |
255.180 |
0.00 |
|
Internal perimeter, Pi cm |
0.000 |
0.000 |
— |
|
External perimeter, Pe cm |
255.180 |
255.180 |
0.00 |
|
Polar moment of inertia, Ip cm4 |
4005530.633 |
3993669.583 |
0.30 |
|
Polar radius of gyration, ip cm |
29.155 |
29.136 |
0.07 |
|
Polar section modulus, Wp cm3 |
80110.800 |
79872.926 |
0.30 |
Notes: Geometric properties of the solid elliptical cross-section of the rod can be determined analytically by the following formulas:
\[ A=\pi \cdot a\cdot b; \] \[ A_{v,y} =\frac{3\cdot \left( {1+\nu } \right)^{2}\cdot \left( {a^{2}+3\cdot b^{2}} \right)^{2}\cdot b^{2}}{\left( {1+\nu } \right)^{2}\cdot \left( {22\cdot a^{2}+30\cdot b^{2}} \right)\cdot b^{4}+\left( {2\cdot \nu ^{2}\cdot a^{2}+\left( {4+8\cdot \nu +10\cdot \nu^{2}} \right)\cdot b^{2}} \right)\cdot a^{4}}\cdot \pi \cdot a\cdot b; \] \[ A_{v,z} =\frac{3\cdot \left( {1+\nu } \right)^{2}\cdot \left( {3\cdot a^{2}+b^{2}} \right)^{2}\cdot a^{2}}{\left( {1+\nu } \right)^{2}\cdot \left( {30\cdot a^{2}+22\cdot b^{2}} \right)\cdot a^{4}+\left( {\left( {4+8\cdot \nu +10\cdot \nu^{2}} \right)\cdot a^{2}+2\cdot \nu^{2}\cdot b^{2}} \right)\cdot b^{4}}\cdot \pi \cdot a\cdot b; \] \[ \alpha =0; \quad I_{y}=I_{v} =I_{1} =\frac{\pi \cdot a\cdot b^{3}}{4}; \quad I_{z} =I_{u} =I_{2} =\frac{\pi \cdot a^{3}\cdot b}{4}; \] \[ I_{t} =\frac{\pi \cdot a^{3}\cdot b^{3}}{a^{2}+b^{2}}; \quad I_{w} =\frac{\pi \cdot a^{3}\cdot b^{3}}{24}\cdot \left( {\frac{a^{2}-b^{2}}{a^{2}+b^{2}}} \right)^{2}; \] \[ i_{y} =i_{v} =\frac{b}{2}; \quad i_{z} =i_{u} =\frac{a}{2}; \] \[ W_{u+} =W_{u-} =\frac{\pi \cdot a^{2}\cdot b}{4}; \quad W_{v+} =W_{v-} =\frac{\pi \cdot a\cdot b^{2}}{4}; \] \[ W_{pl,u} =\frac{4\cdot a^{2}\cdot b}{3}; \quad W_{pl,v} =\frac{4\cdot a\cdot b^{2}}{3}; \] \[ a_{u+} =a_{u-} =\frac{b}{4}; \quad a_{v+} =a_{v-} =\frac{a}{4}; \] \[ y_{m} =y_{b} =z_{m} =z_{b} =0; \] \[P=P_{e} =4\cdot a\cdot E\left( {\frac{\sqrt {a^{2}-b^{2}} }{a}} \right), \quad where:\quad E\left( x \right) \text {Legendre complete elliptic integral of the second kind;} \] \[ P\approx 4\cdot \left( {a+b} \right)-\frac{2\cdot \left( {4-\pi } \right)\cdot a\cdot b}{\sqrt[{\frac{3\cdot \pi -8}{8-2\cdot \pi }}]{\frac{a^{\frac{3\cdot \pi -8}{8-2\cdot \pi }}+b^{\frac{3\cdot \pi -8}{8-2\cdot \pi }}}{2}}}; \quad P\approx \pi \cdot \left( {a+b} \right); \quad P_{i} =0; \] \[ I_{12} =0; \quad I_{p} =\frac{\pi \cdot a\cdot b\cdot \left( {a^{2}+b^{2}} \right)}{4}; \quad i_{p} =\frac{\sqrt {a^{2}+b^{2}} }{2}; \quad W_{p} =\frac{\pi \cdot b\cdot \left( {a^{2}+b^{2}} \right)}{4}. \]