Geometric Properties of an Equilateral Triangle
Aim: To check the accuracy of the geometric properties calculation for a rod cross-section in the form of an equilateral triangle.
Name of a file with the initial data: Triangle.cns
Formulation: Check the accuracy of the torsional geometric properties calculation for a rod cross-section in the form of an equilateral triangle.
References: Young W.C., Budynas R.G., Roark's Formulas for Stress and Strain, New York , McGraw-Hill, New York, 2002.
Initial data:
| ν = 0.3 | - Poisson’s ratio; |
| a = 40 cm | - side length of an equilateral triangle. |
Design model: The design model is created by triangulation (the number of triangles ≈ 3000) on the basis of a model of the external contour. The external contour is an equilateral triangle. The number of vertices of the contour in a model is 3.
Results Obtained in Consul
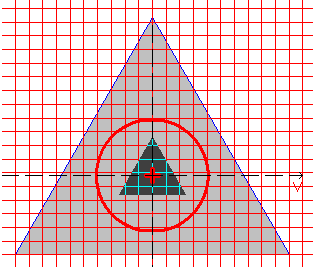
Design model, coordinate and principal axes, center of mass, ellipse of inertia, core of the section
Comparison of results:
|
Parameter |
Theory |
CONSUL |
Deviation, % |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Torsional moment of inertia, It cm4 |
55425,625 |
54477,143 |
1.71 |
|
Y-coordinate of the shear center, yb cm |
20 |
19,999 |
0,005 |
|
Z-coordinate of the shear center, zb cm |
11,547 |
11,589 |
0,36 |
Notes: Geometric properties can be determined analytically by the following formulas:
\[ I_{t} =\frac{\sqrt 3 }{80}a^{4}; \] \[ y_{b} =a/2; \] \[ z_{b} =\frac{a}{2\sqrt 3 }. \]