Geometric Properties of Regular Polygons
|
pentagon |
|
|
|
hexagon |
|
|
|
octagon |
|
|
Aim: To check the accuracy of the torsional moment of inertia calculation for a rod cross-section in the form of a regular polygon.
| Names of files with the initial data: | Pentagon.cns Hexagon.cns Octagon.cns |
Formulation: Check the accuracy of the torsional geometric properties calculation for a rod cross-section in the form of a regular pentagon, hexagon and octagon.
References: Hassenpflug W.C., Torsion of uniform bars with polygon cross-section, Computers & Mathematics with Applications, 2003, 46, No. 2-3, 313–392.
Kovář A., Moment tuhosti v kroucení pravidelného pětiúhelníka, Aplikace matematiky, 1957, 2, No. 1, 58-65.
Initial data:
| ν = 0.3 | - Poisson’s ratio; |
| r = 10 cm | - radius of a circumscribed circle. |
Design model: The design model is created by triangulation (the number of triangles ≈ 3000) on the basis of a model of the external contour. The external contour is a regular polygon. The number of vertices of the contour in a model is 5 (6, 8).
Results Obtained in Consul
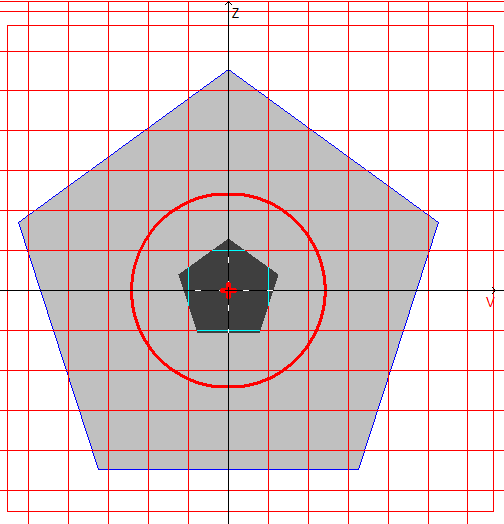
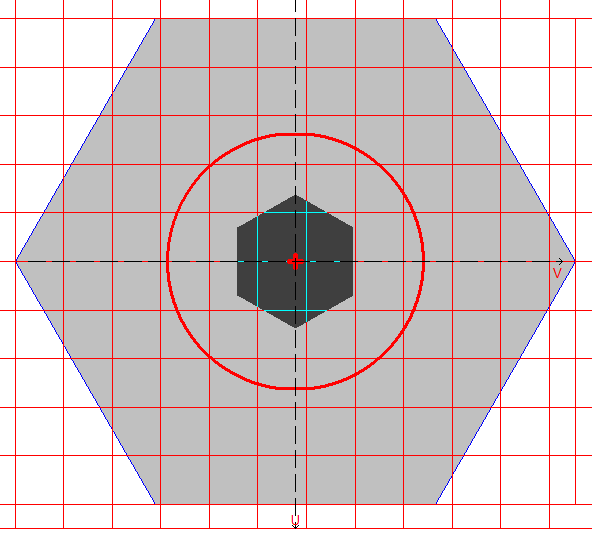
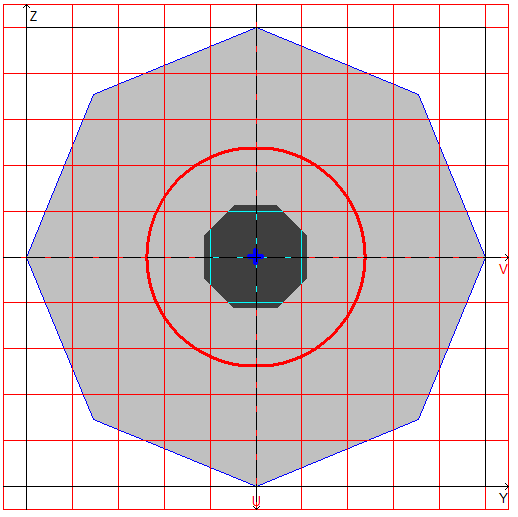
Design model, coordinate and principal axes, center of mass, ellipse of inertia, core of the section
Comparison of results:
|
|
Parameter |
Theory |
CONSUL |
Deviation, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
pentagon |
Torsional moment of inertia, It cm4 |
8478,1 |
8312,915 |
1,98 |
|
hexagon |
10384 |
10215,966 |
1,61 |
|
|
octagon |
12556,6 |
12453,297 |
0,822 |
Notes: Geometric properties can be determined analytically by the following formulas:
\[ \text {пятиугольник }\quad I_{t} \approx \mbox{0,84781}r^{4}; \]
\[ \text {шестиугольник}\quad I_{t} \approx \mbox{1,03877}r^{4}; \]
\[ \text {воcьмиугольник}\quad I_{t} \approx \mbox{1,25566}r^{4}; \]