Geometric Properties of a Square with a Central Square Hole

Aim: To check the accuracy of the torsional moment of inertia calculation for the cross-section of a rod with a hole.
Name of a file with the initial data: SquareWithHole.cns
Formulation: Check the accuracy of the torsional geometric properties calculation for a rod cross-section in the form of a square with a central square hole.
References: Arutiunian N.H., Abramian B.L., Torsion of Elastic Bodies, M., Fizmatgiz,, 1963 (see § III.1.7).
Initial data:
| ν = 0.3 | - Poisson’s ratio; |
| b = 100 cm | - geometric dimansions. |
| d = 40 cm |
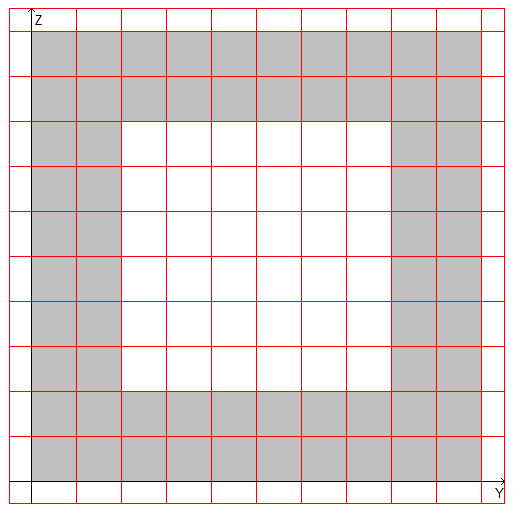
Design model: The design model is formed by triangulation (the number of triangles ≈ 3000) on the basis of a model of the external contour. The external contour is a square, the internal one is a central square. The number of vertices of the contour in a model is 8.
Results Obtained in Consul
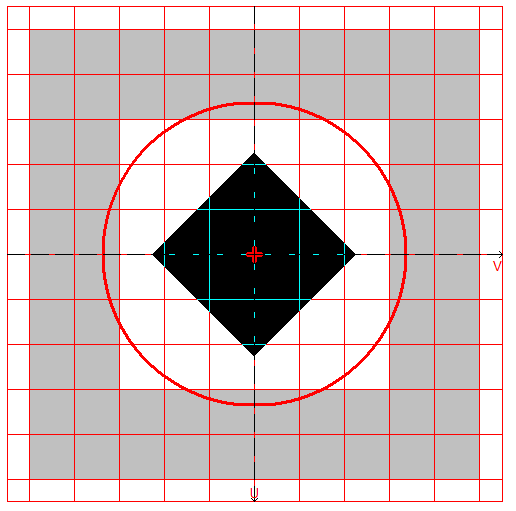
Design model, coordinate and principal axes, center of mass, ellipse of inertia, core of the section
Comparison of results:
|
Parameter |
Theory |
CONSUL |
Deviation, % |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Torsional moment of inertia, It cm4 |
189095936 |
188022747,341 |
0,56 |
Notes: Geometric properties can be determined analytically by the following formulas:
\[ I_{t} \approx 8\left[ {\left( {\frac{b}{d}} \right)^{3}-1,2704\left( {\frac{b}{d}} \right)^{2}+0,661\left( {\frac{b}{d}} \right)-0,1043} \right]d^{4}. \]