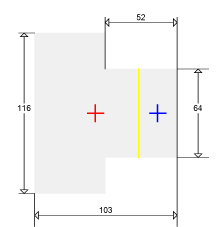
Calculation of the T-section Wall Segment for Load-bearing Capacity and Crack Opening – Rigid Supports
Objective: Check of the calculation of eccentrically compressed columns.
Task: Verify the correctness of the analysis of stability and masonry seam opening under eccentric compression.
References: Reference manual on design of masonry and reinforced masonry structures (supplement to SNiP II-22-81), 1989, p. 20-21.
Initial data file:
|
1. when the longitudinal force is N = 326 kN: |
Example 3.1.SAV; |
|
2. when the longitudinal force is N = 160 kN: |
Example 3.2.SAV |
Initial data:
| е0 = -0,45 m | Force eccentricity |
| Н = 5 m |
Storey height |
| Stone/brick | Molded clay brick, grade 100 |
| Mortar | Regular cement with mineral plasticizers, grade 50 |
| R = 1,5 MPa | Design resistance of masonry |
| Нf = 0,22 m | Thickness of the precast reinforced concrete floor slab, embedded into wall masonry on the supports |
KAMIN initial data when the longitudinal force is N = 326 kN:
Importance factor γn = 1
Age of masonry - up to a year
Working life is 50 years
Stone/brick - Molded clay brick
Stone/brick grade - 100
Mortar - regular cement with mineral plasticizers
Mortar grade - 50
Structure:
|
|
Eccentricity of longitudinal force - 45 cm along the Y axis |
|
Effective height in the XoY plane |
Effective height in the XoZ plane |
|---|---|
|
Bracing scheme |
Bracing scheme |
KAMIN initial data when the longitudinal force is N = 160 kN:
Importance factor γn = 1
Age of masonry - up to a year
Working life is 50 years
Stone/brick - Molded clay brick
Stone/brick grade - 100
Mortar - regular cement with mineral plasticizers
Mortar grade - 50
Structure:
|
|
Eccentricity of longitudinal force - 45 cm along the Y axis |
|
Effective height in the XoY plane |
Effective height in the XoZ plane |
|---|---|
|
Bracing scheme |
Bracing scheme |
Comparison of solutions:
|
Longitudinal force |
N = 326 kN |
N = 160 kN |
|
Check |
stability |
masonry seam opening |
|
Theory |
326/326 = 1 |
160/160 = 1 |
|
KAMIN |
0,958 |
0,999 |
|
Deviation, % |
0,398 |
0,1 |
Comments:
- Specific value of the applied longitudinal force is not determined in the problem, therefore KAMIN uses the calculated values of the load-bearing capacity N = 326 kN and N = 160 kN for stability and masonry seam opening respectively.
- The column height in KAMIN is taken as the difference between the storey height and the floor slab thickness Н - Нf = 5 – 0,22 = 4,78 m.
- Distance between transverse rigid structures has to be specified in KAMIN. Since it is not determined in the problem, the value of 5 m is used.
- Age of masonry has to be specified in KAMIN. Since it is not determined in the problem, the value of "up to a year" is used.