Calculation of the Load-bearing Capacity of the Basement Wall of a Brick Building
Application of vertical loads
Objective: Check the calculation of the basement wall.
Task: Verify the correctness of the analysis of stability in the eccentricity plane under eccentric compression of the section with the maximum bending moment.
References: Reference manual on design of masonry and reinforced masonry structures (supplement to SNiP II-22-81), 1989, p. 81-82.
Initial data file:
ComeIn 18.doc — report
Initial data:
Mortar
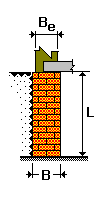
| H = 2,8 m | Height of the basement wall; |
| b×h = 0,4×0,58 m |
Dimensions of concrete blocks; |
| Aп = 25 % | Void percentage of blocks over the area of the middle horizontal cross-section; |
| Vп = 15 % | Void percentage of blocks over the volume; |
| l0 = 2,65 m | Effective height of the basement wall; |
| b1 = 0,51 m | Thickness of the first floor brick wall; |
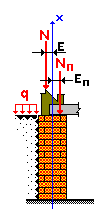
| N1 = 150 kN | Design load per 1 m of the basement wall from the first floor wall; |
| е1 = 5,5 cm | Eccentricity of the load from the first floor wall; |
| N2 = 22 kN | Design load per 1 m of the basement wall from the floor slab above the basement bearing on this wall; |
| е2 = 16 cm | Eccentricity of the load from the floor slab above the basement bearing on the basement wall; |
| γ = 16 kN/m3 | Specific weight of fill-up soil; |
| φ = 38° | Design internal friction angle of soil; |
| p = 10 kN/m2 | Characteristic value of the surface load from the fill-up soil; |
| Stone/brick | Large hollow concrete blocks, grade 100; |
| Regular cement with mineral plasticizers, grade 50. |
KAMIN initial data:
Importance factor γn = 1
Age of masonry - up to a year
Working life is 25 years
Stone/brick - Large concrete blocks, 500 mm ≤ Н ≤ 1000 mm
Stone/brick grade - 100
Mortar - regular cement with mineral plasticizers
Mortar grade - 50
Reduction factor 0,5
Specific weight of masonry 22,44 kN/m3
Structure:
|
|
L = 2,65 m |
Loads per unit length
|
|
Load on surface 12 kN/m2 Loads from the above floor slabs |
Comparison of solutions:
|
Check |
stability under eccentric compression of the middle cross-section |
|
Theory |
181,5/380 = 0,478 |
|
KAMIN |
0,481 |
|
Deviation, % |
0,624 |
Comments:
- The manual uses characteristic values of the load on surface and specific weight of soil, which are then multiplied by the corresponding overload factors n1 = n2 = 1,2. Their obtained design values are used in KAMIN: p ∙ n1 = 10∙1,2 = 12 kN/m2 and γ ∙ n2 = 16∙1,2 = 19,2 N/m3 respectively.
- The value of the specific weight of soil is obtained by multiplying the specific weight of concrete 24 kN/m3 by a factor of 0,85, taking into account the void percentage of blocks over the volume Vv=15 %, and the overload factor for masonry structures 1,1: γm = 24∙0,85∙1,1 = 22,44 kN/m3.
- Age of masonry and working life have to be specified in KAMIN. Since they are not determined in the problem, the following data are used: "up to a year" and 50 years respectively.
- The column height has to be specified in KAMIN. Since the effective column height determined in the problem is 3 m, this value is used for the column height at the effective height factors equal to 1.