Three-Step Simply Supported Beam Subjected to Concentrated Forces
Objective: Strain state of a three-step simply supported beam subjected to concentrated forces without taking into account the transverse shear deformations. Transverse displacements and rotation angles are checked.
Initial data file: 4_5.spr
Problem formulation: The three-step simply supported beam is subjected to three concentrated forces Р. Determine the rotation angles of support sections and transverse displacements in the force application points.
References: G.S. Pisarenko, A.P. Yakovlev, V.V. Matveev, Handbook on Strength of Materials. — Kiev: Naukova Dumka, 1988.
Initial data:
| E = 2.0·1011 Pa | - elastic modulus, |
| l = 1 m | - half length of the beam span of each section; |
| F = 1·10-2 m2 | - cross-sectional area; |
| I1 = 5·10-6 m4 | - moment of inertia; |
| Р = 1 kN | - load value. |
| I1 : I2 : I3 = 1 : 2 : 3 | |
| F1 : F2 :F3 = 1 : 2 : 3 |
Finite element model: Design model – general type system, 6 bar elements of type 5, 7 nodes.
Results in SCAD
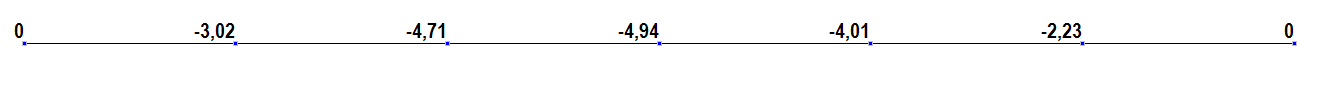
Values of transverse displacements w (mm)

Values of rotation angles θ (rad)
Comparison of solutions:
|
Parameter |
Theory |
SCAD |
Deviations, % |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Transverse displacements, mm w (l) w (3l) w (5l) |
-3.02 -4.94 -2.23 |
-3.02 -4.94 -2.23 |
0.00 0.00 0.00 |
|
Rotation angles, rad θ (0) θ (6l) |
0.00327 -0.00231 |
0.00327 -0.00231 |
0.00 0.00 |
Notes: In the analytical solution, the rotation angles of support sections and deflections in the force application points are determined according to the following formulas:
\[ w\left( l \right)=-\frac{653\cdot P\cdot l^{3}}{216\cdot E\cdot I_{1} }; \quad w\left( {3\cdot l} \right)=-\frac{89\cdot P\cdot l^{3}}{18\cdot E\cdot I_{1} }; \quad w\left( {5\cdot l} \right)=-\frac{481\cdot P\cdot l^{3}}{216\cdot E\cdot I_{1} }; \] \[ \theta \left( 0 \right)=\frac{707\cdot P\cdot l^{2}}{216\cdot E\cdot I_{1} }; \quad \theta \left( {6\cdot l} \right)=-\frac{499\cdot P\cdot l^{2}}{216\cdot E\cdot I_{1} }. \]
