Simply Supported Flat Rectangular Plate Subjected to a Transverse Load Uniformly Distributed over the Entire Area and a Concentrated Shear Force Applied in the Center
Objective: Check of the obtained values of the transverse displacements in the center of a simply supported flat rectangular plate subjected to a transverse load uniformly distributed over the entire area and a concentrated shear force applied in the center.
Initial data files:
|
File name |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Design model with the elements of type 42 for meshes 2x2, 4x4, 8x8 |
|
|
Design model with the elements of type 44 for meshes 2x2, 4x4, 8x8 |
|
|
Design model with the elements of type 45 for meshes 2x2, 4x4, 8x8 |
|
|
Design model with the elements of type 50 for meshes 2x2, 4x4, 8x8 |
|
|
Bending_of_rectangular_flat_plate_Simply_supported_Solid_36_Mesh_16x16.SPR Bending_of_rectangular_flat_plate_Simply_supported_Solid_36_Mesh_32x32.SPR Bending_of_rectangular_flat_plate_Simply_supported_Solid_36_Mesh_64x64.SPR Bending_of_rectangular_flat_plate_Simply_supported_Solid_36_Mesh_128x128.SPR |
Design model with the elements of type 36 for meshes 2x2, 4x4, 8x8, 16x16, 32x32, 64x64, 128x128 |
|
Bending_of_rectangular_flat_plate_Simply_supported_Solid_37_Mesh_16x16.SPR Bending_of_rectangular_flat_plate_Simply_supported_Solid_37_Mesh_32x32.SPR Bending_of_rectangular_flat_plate_Simply_supported_Solid_37_Mesh_64x64.SPR Bending_of_rectangular_flat_plate_Simply_supported_Solid_37_Mesh_128x128.SPR |
Design model with the elements of type 37 for meshes 2x2, 4x4, 8x8, 16x16, 32x32, 64x64, 128x128 |
Problem formulation: The simply supported flat rectangular plate is subjected to the transverse load q uniformly distributed over the entire area and the concentrated shear force P applied in the center. Check the obtained values of the transverse displacements in the center of the simply supported flat rectangular plate wq and wP from the respective actions.
References: R. H. Macneal, R. L. Harder, A proposed standard set of problems to test finite element accuracy, North-Holland, Finite elements in analysis and design, 1, 1985, p. 3-20.
S. Timoshenko, S. Woinowsky-Krieger, Theory of plates and shells, New York, McGraw-Hill,1959, p. 120, 143, 202, 206.
Initial data:
| E = 1.7472·107 kPa | - elastic modulus of the plate material; |
| ν = 0.30 | - Poisson’s ratio; |
| a = 2.00 m | - width of the plate; |
| b = 10.00 m | - length of the plate; |
| h = 10-4 (10-2) m | - thickness of the plate; |
| q = 1.0·10-4 kN/m2 | - value of the transverse load uniformly distributed over the entire area of the plate; |
| P = 4.0·10-4 kN | - value of the concentrated shear force in the center of the plate. |
Finite element model: Design model – general type system. Six design models of a quarter of the plate according to the symmetry conditions are considered:
Model 1 – 8, 32, 128 three-node shell elements of type 42 with a regular mesh 2x2, 4x4, 8x8. The thickness of the plate – 10-4 m. Boundary conditions are provided by imposing constraints on the nodes of the support edges of the plate in the directions of the degrees of freedom X, Y, Z and constraints according to the symmetry conditions. Number of nodes in the model – 9, 25, 81.
Model 2 – 4, 16, 64 four-node shell elements of type 44 with a regular mesh 2x2, 4x4, 8x8. The thickness of the plate – 10-4 m. Boundary conditions are provided by imposing constraints on the nodes of the support edges of the plate in the directions of the degrees of freedom X, Y, Z and constraints according to the symmetry conditions. Number of nodes in the model – 9, 25, 81.
Model 3 – 8, 32, 128 six-node shell elements of type 45 with a regular mesh 2x2, 4x4, 8x8. The thickness of the plate – 10-4 m. Boundary conditions are provided by imposing constraints on the nodes of the support edges of the plate in the directions of the degrees of freedom X, Y, Z and constraints according to the symmetry conditions. Number of nodes in the model – 25, 81, 289.
Model 4 – 4, 16, 64 eight-node shell elements of type 50 with a regular mesh 2x2, 4x4, 8x8. The thickness of the plate – 10-4 m. Boundary conditions are provided by imposing constraints on the nodes of the support edges of the plate in the directions of the degrees of freedom X, Y, Z and constraints according to the symmetry conditions. Number of nodes in the model – 25, 81, 289.
Model 5 – 4, 16, 64, 256, 1024, 4096, 16384 eight-node isoparametric solid elements of type 36 with a regular mesh 2x2x1, 4x4x1, 8x8x1, 16x16x1, 32x32x1, 64x64x1, 128x128x1. The thickness of the plate – 10-2 m. Boundary conditions are provided by imposing constraints on the nodes of the support sides of the lower surface of the plate in the direction of the degree of freedom Z and constraints according to the symmetry conditions. Number of nodes in the model – 18, 50, 162, 578, 2178, 8450, 33282.
Model 6 – 4, 16, 64, 256, 1024, 4096, 16384 twenty-node isoparametric solid elements of type 37 with a regular mesh 2x2x1, 4x4x1, 8x8x1, 16x16x1, 32x32x1, 64x64x1, 128x128x1. The thickness of the plate – 10-2 m. Boundary conditions are provided by imposing constraints on the nodes of the support sides of the lower surface of the plate in the direction of the degree of freedom Z and constraints according to the symmetry conditions. Number of nodes in the model – 51, 155, 531, 1955, 7491, 29315, 115971.
Results in SCAD
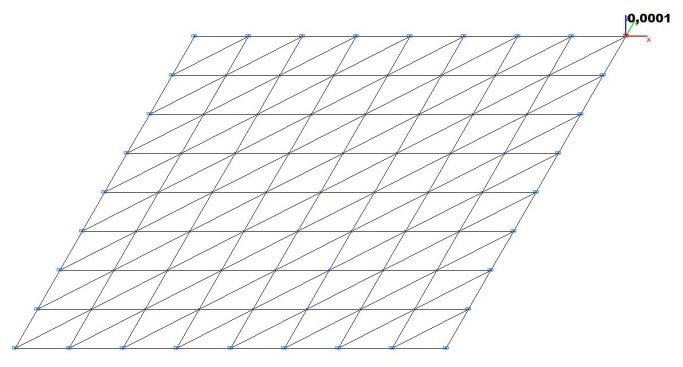
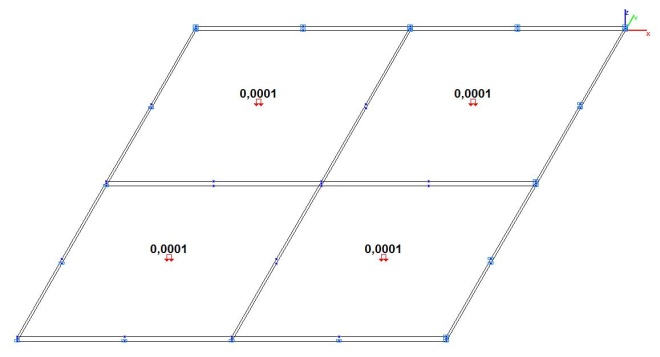
Model 1. Design model
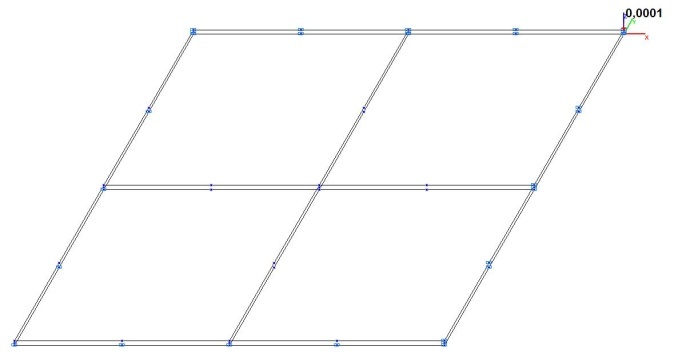
Model 1. Deformed model
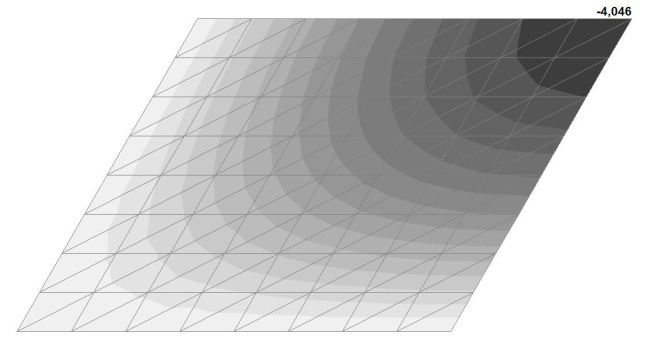
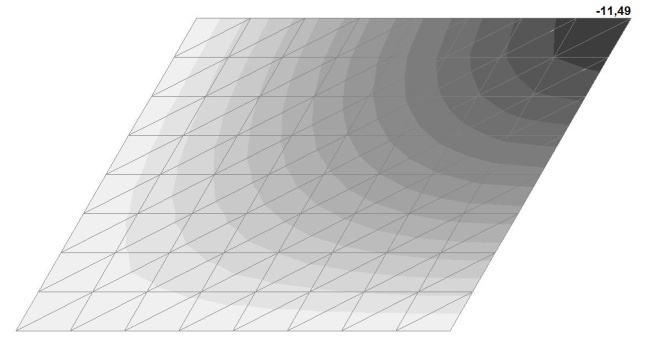
Model 1. Values of the transverse displacements in the center of the simply supported rectangular plate wq and wP (m, m)
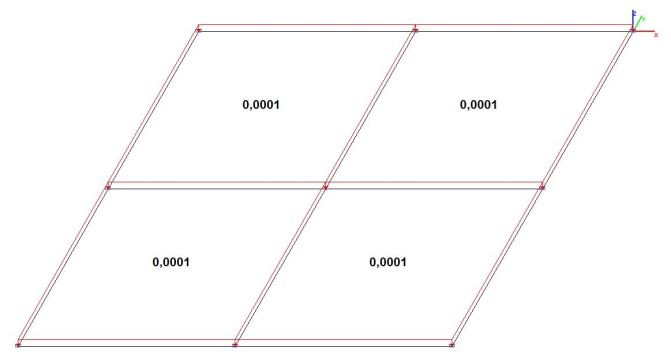
Model 2. Design model
Model 2. Deformed model
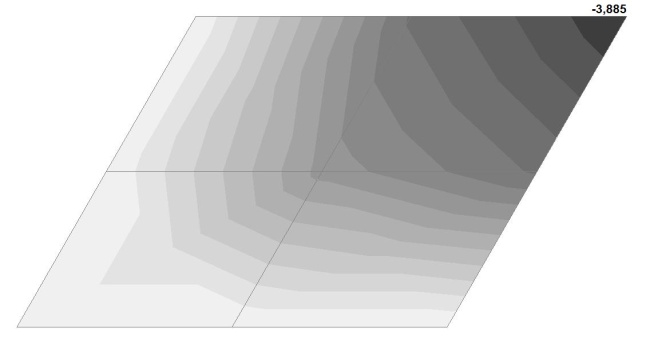
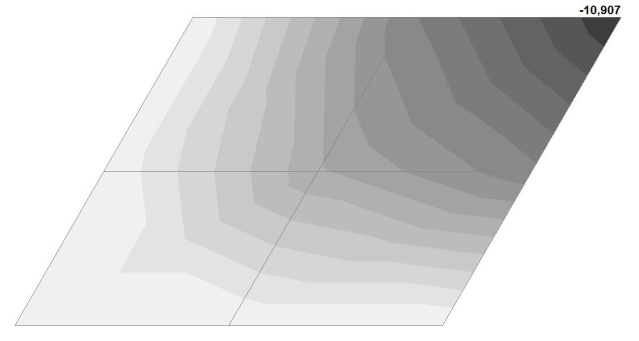
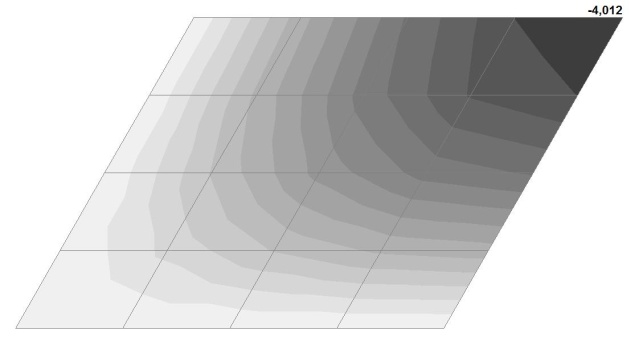
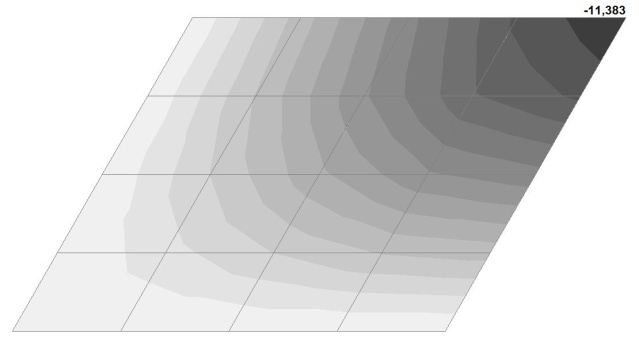
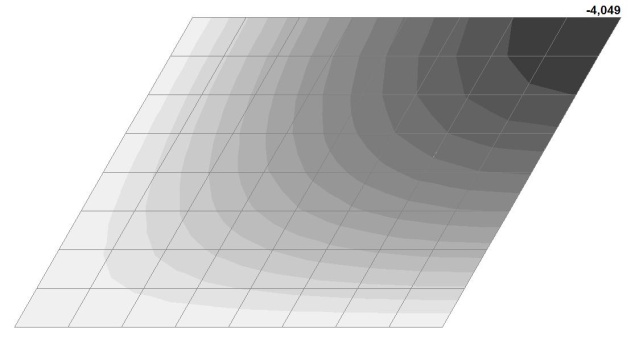
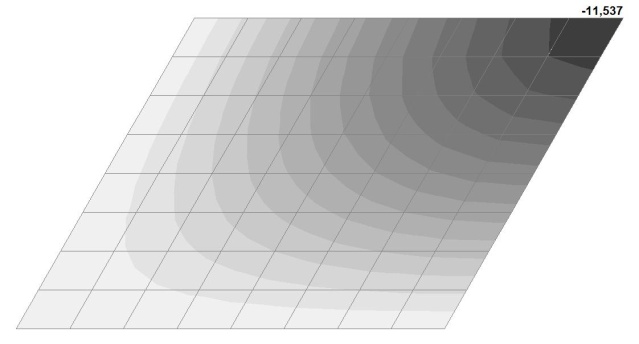
Model 2. Values of the transverse displacements in the center of the simply supported rectangular plate wq and wP (m, m)
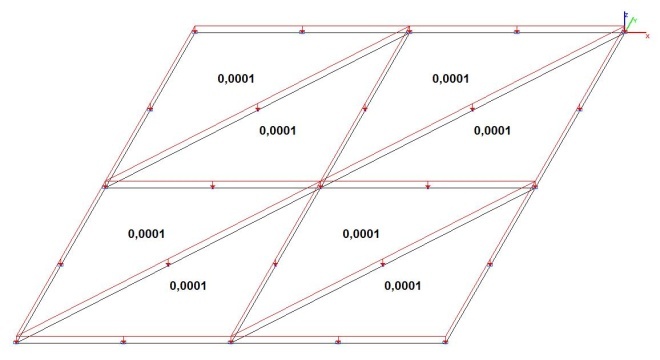
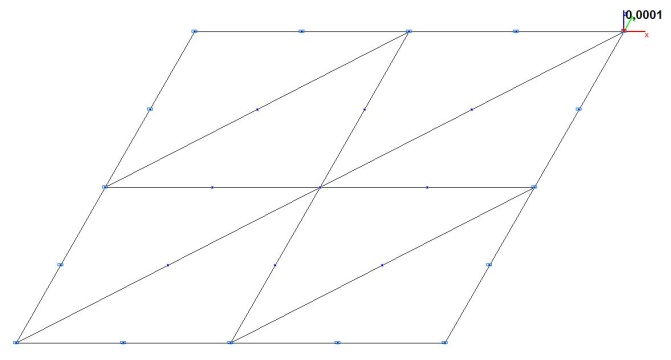
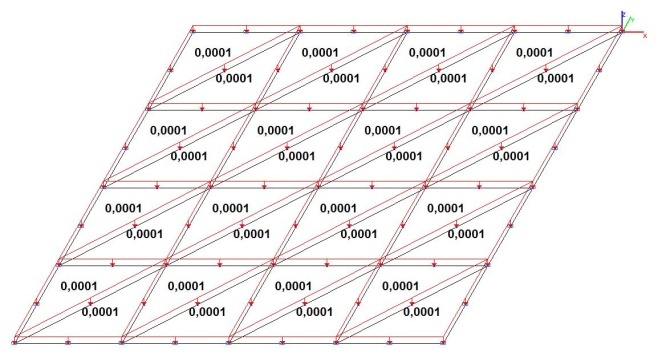
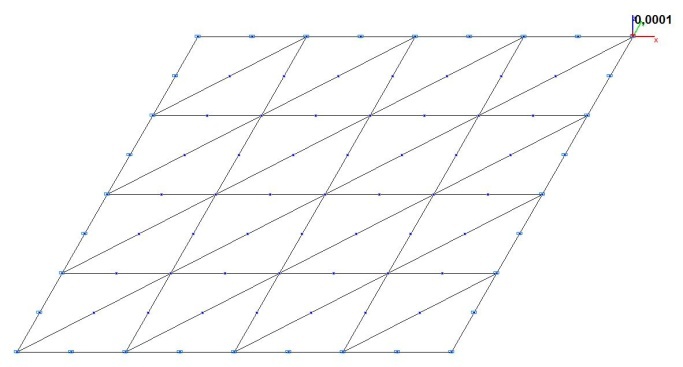
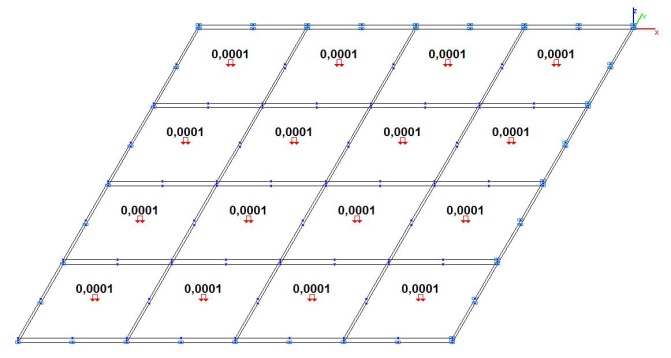
Model 3. Design model

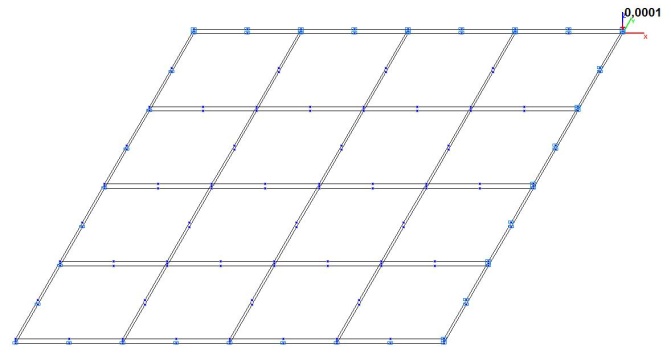
Model 3. Deformed model
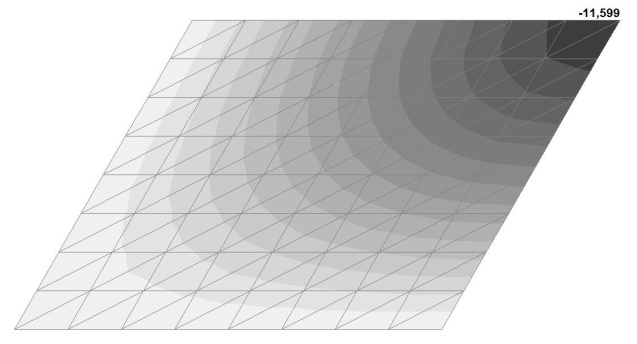
Model 3. Values of the transverse displacements in the center of the simply supported rectangular plate wq and wP (m, m)
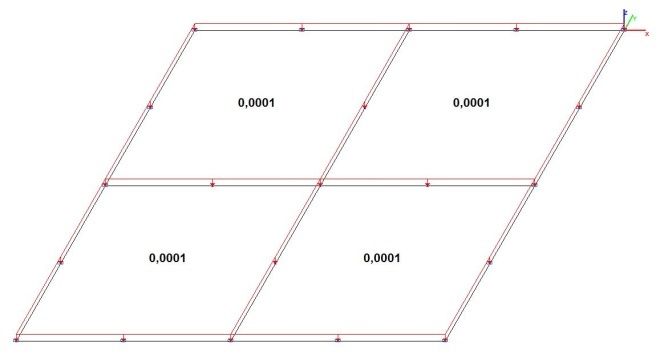
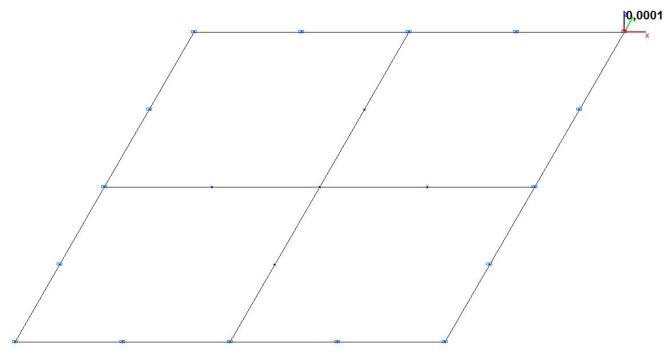
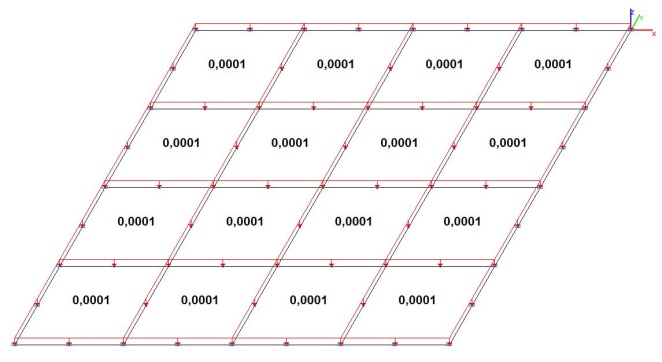

Model 4. Design model
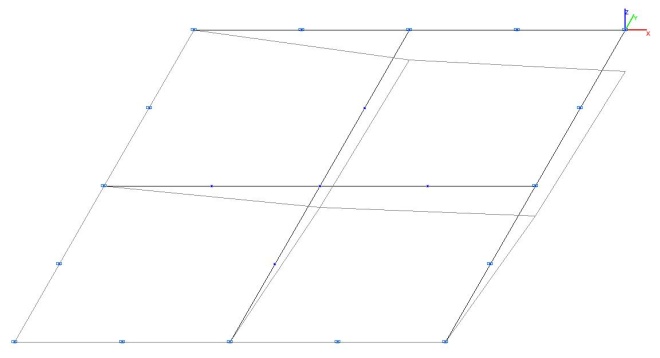
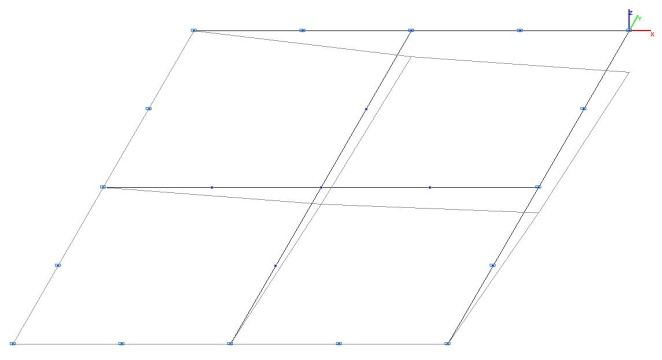
Model 4. Deformed model
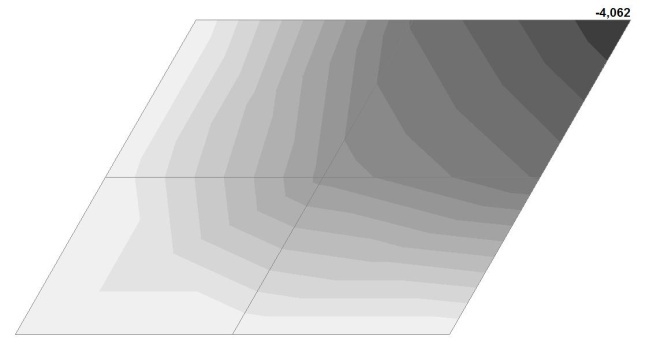
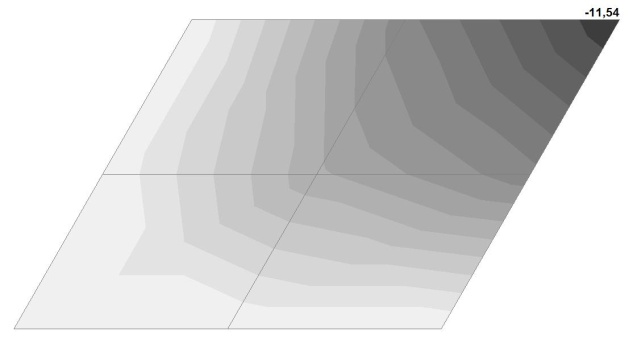
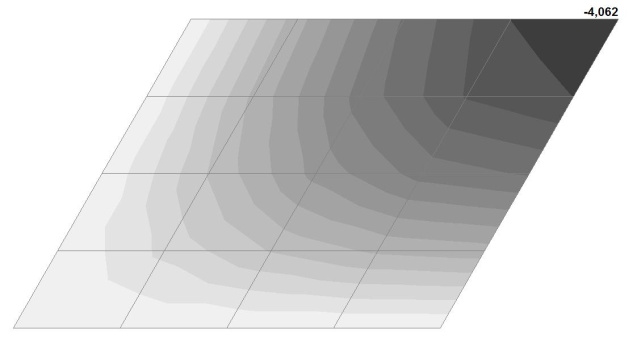
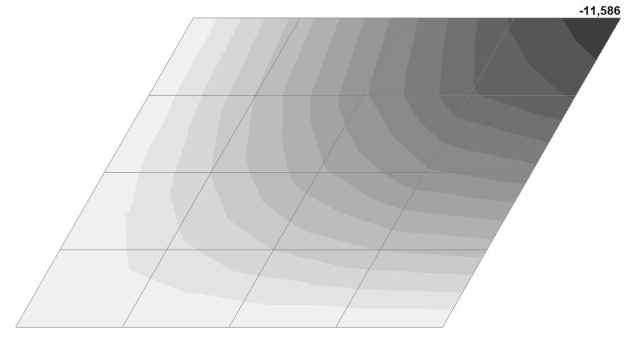
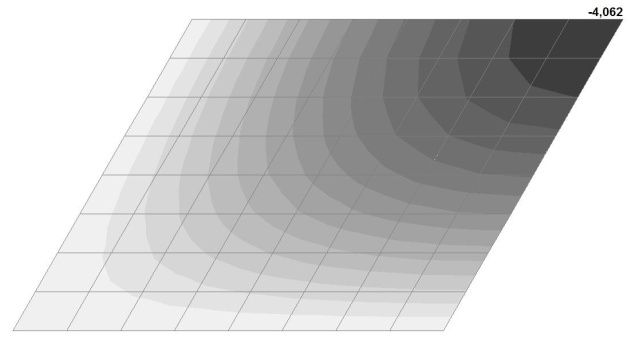
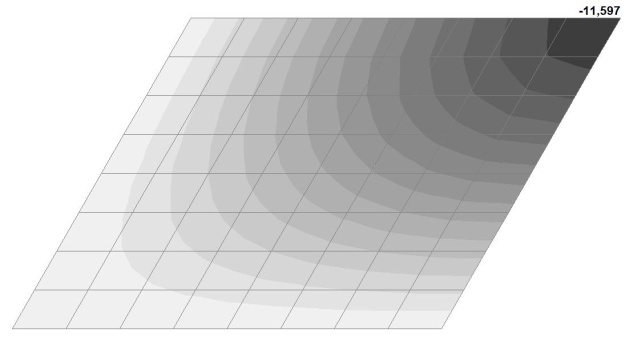
Model 4. Values of the transverse displacements in the center of the simply supported rectangular plate wq and wP (m, m)
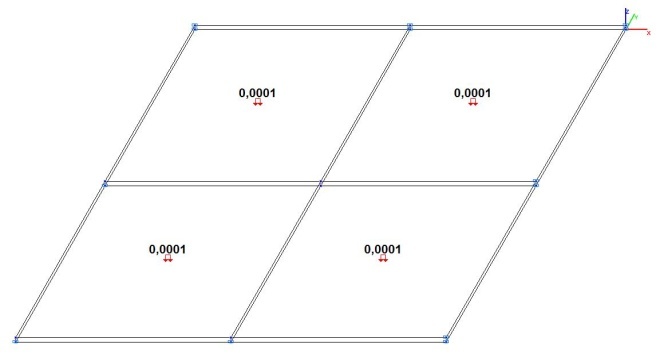
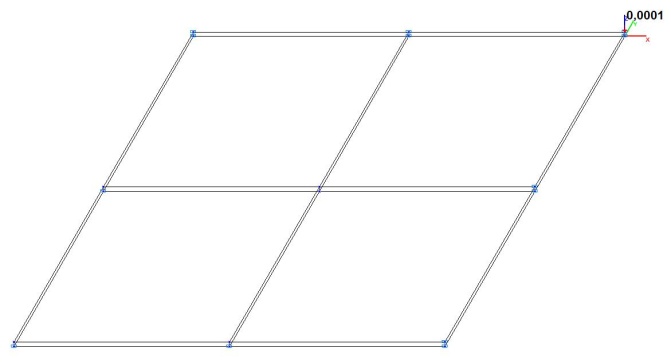
Model 5. Design model
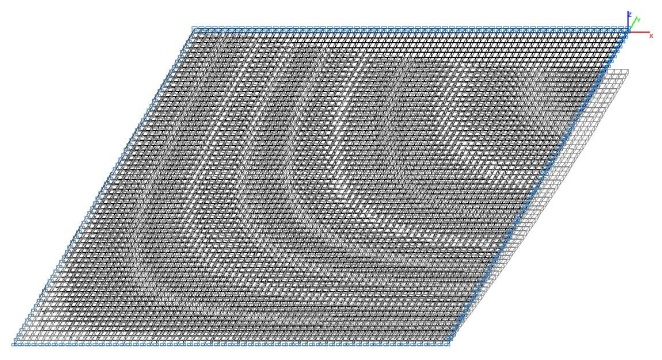
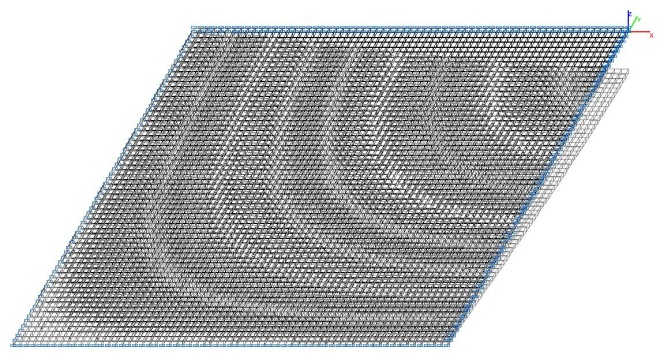
Model 5. Deformed model
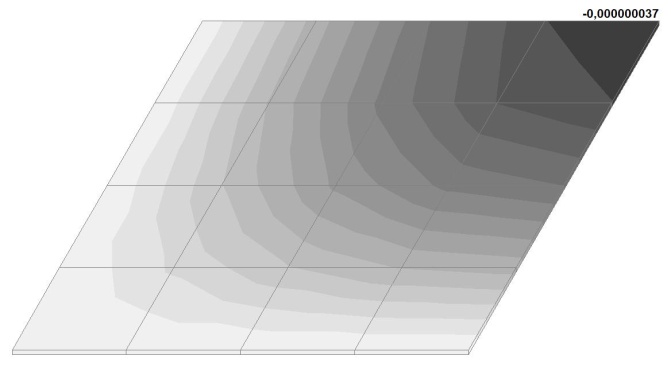
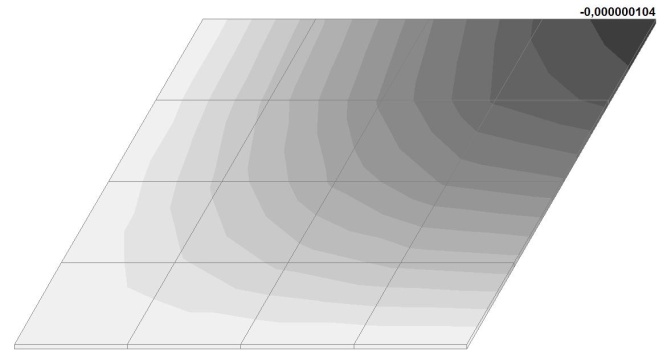
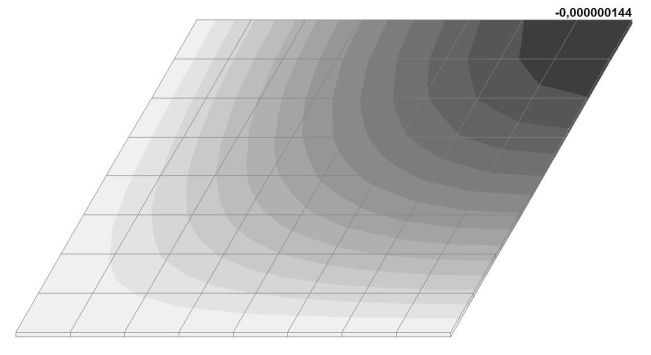
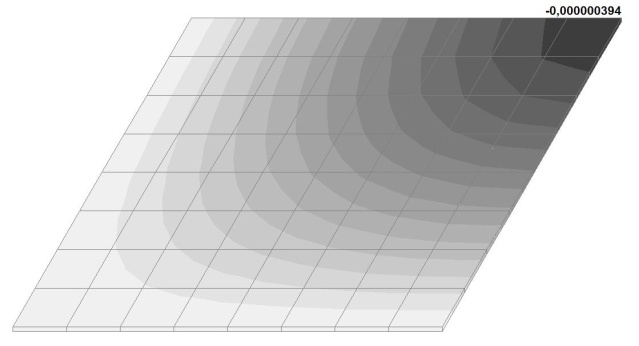
Model 5. Values of the transverse displacements in the center of the simply supported rectangular plate wq and wP (m, m)
Model 6. Design model
Model 6. Deformed model
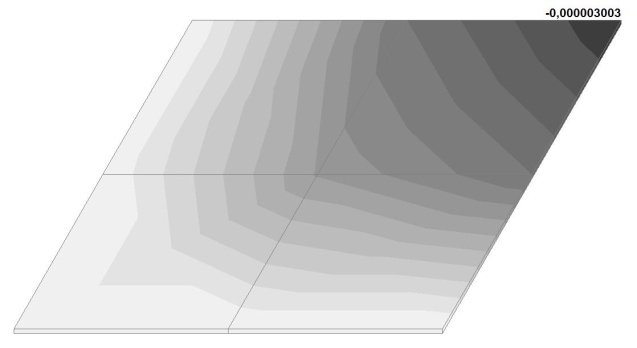
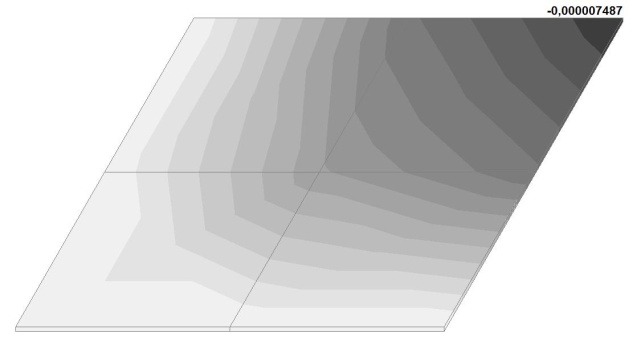
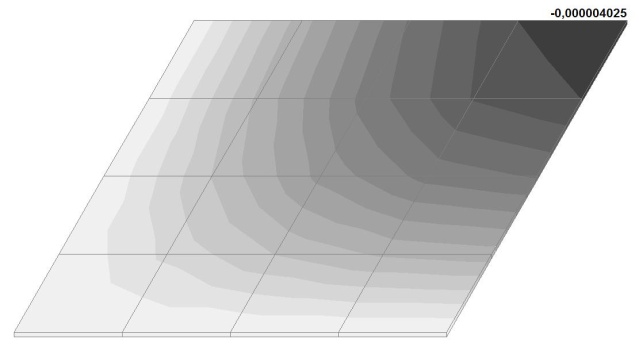
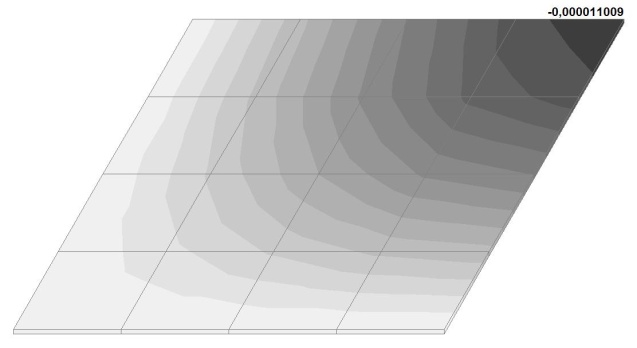
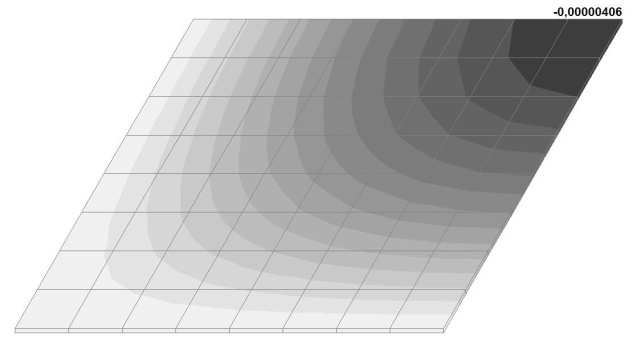
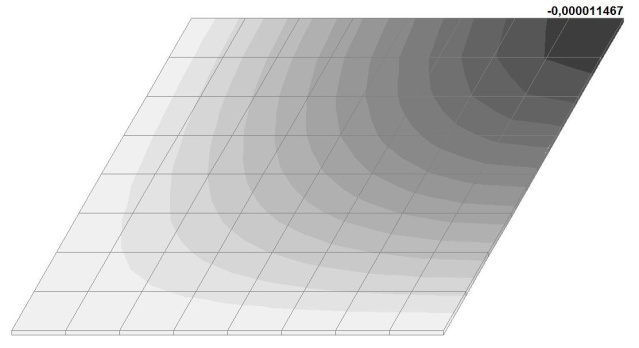
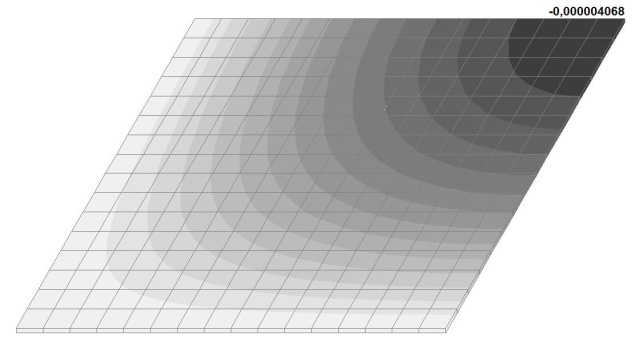
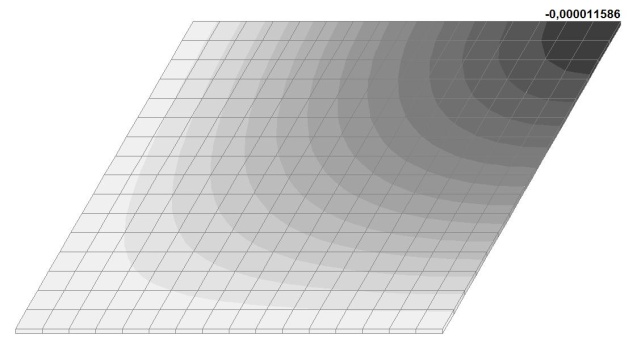
Model 6. Values of the transverse displacements in the center of the simply supported rectangular plate wq and wP (m, m)
Comparison of solutions:
Transverse displacements in the center of the simply supported flat rectangular plate wq from the transverse load q uniformly distributed over the entire area
|
Model |
Finite element mesh |
Theory |
SCAD |
Deviation, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1 (Member type 42) |
2x2 |
12.971 |
11.804 |
9.00 |
|
4x4 |
12.847 |
0.96 |
||
|
8x8 |
12.958 |
0.10 |
||
|
2 (Member type 44) |
2x2 |
12.971 |
12.528 |
3.42 |
|
4x4 |
13.093 |
0.94 |
||
|
8x8 |
13.030 |
0.45 |
||
|
3 (Member type 45) |
2x2 |
12.971 |
13.029 |
0.45 |
|
4x4 |
12.973 |
0.02 |
||
|
8x8 |
12.971 |
0.00 |
||
|
4 (Member type 50) |
2x2 |
12.971 |
13.020 |
0.38 |
|
4x4 |
12.971 |
0.00 |
||
|
8x8 |
12.971 |
0.00 |
||
|
5 (Member type 36) |
2x2 |
12.971∙10-6 |
0.017∙10-6 |
99.87 |
|
4x4 |
0.067∙10-6 |
99.48 |
||
|
8x8 |
0.264∙10-6 |
97.96 |
||
|
16x16 |
0.983∙10-6 |
92.42 |
||
|
32x32 |
3.099∙10-6 |
76.11 |
||
|
64x64 |
6.656∙10-6 |
48.69 |
||
|
128x128 |
9.234∙10-6 |
28.81 |
||
|
6 (Member type 37) |
2x2 |
12.971∙10-6 |
9.000∙10-6 |
30.61 |
|
4x4 |
13.308∙10-6 |
2.60 |
||
|
8x8 |
12.931∙10-6 |
0.31 |
||
|
16x16 |
12.963∙10-6 |
0.06 |
||
|
32x32 |
12.971∙10-6 |
0.00 |
||
|
64x64 |
12.972∙10-6 |
0.01 |
||
|
128x128 |
12.973∙10-6 |
0.02 |
Transverse displacements in the center of the simply supported flat rectangular plate wP from the concentrated shear force P applied in the center
|
Model |
Finite element mesh |
Theory |
SCAD |
Deviation, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1 (Member type 42) |
2x2 |
16.960 |
7.771 |
54.18 |
|
4x4 |
11.983 |
29.34 |
||
|
8x8 |
14.833 |
12.54 |
||
|
2 (Member type 44) |
2x2 |
16.960 |
12.674 |
25.27 |
|
4x4 |
14.768 |
12.92 |
||
|
8x8 |
15.657 |
7.68 |
||
|
3 (Member type 45) |
2x2 |
16.960 |
15.383 |
9.30 |
|
4x4 |
16.539 |
2.48 |
||
|
8x8 |
16.849 |
0.65 |
||
|
4 (Member type 50) |
2x2 |
16.960 |
15.862 |
6.47 |
|
4x4 |
16.553 |
2.40 |
||
|
8x8 |
16.845 |
0.68 |
||
|
5 (Member type 36) |
2x2 |
16.960∙10-6 |
0.014∙10-6 |
99.92 |
|
4x4 |
0.051∙10-6 |
99.70 |
||
|
8x8 |
0.197∙10-6 |
98.84 |
||
|
16x16 |
0.737∙10-6 |
95.65 |
||
|
32x32 |
2.426∙10-6 |
85.70 |
||
|
64x64 |
5.859∙10-6 |
65.45 |
||
|
128x128 |
9.654∙10-6 |
43.08 |
||
|
6 (Member type 37) |
2x2 |
16.960∙10-6 |
4.494∙10-6 |
73.50 |
|
4x4 |
10.523∙10-6 |
37.95 |
||
|
8x8 |
15.480∙10-6 |
8.73 |
||
|
16x16 |
16.572∙10-6 |
2.29 |
||
|
32x32 |
16.866∙10-6 |
0.55 |
||
|
64x64 |
16.952∙10-6 |
0.05 |
||
|
128x128 |
16.976∙10-6 |
0.09 |
Notes: In the analytical solution the values of the transverse displacements in the center of the simply supported flat rectangular plate wq and wP from the respective actions are determined according to the following formulas:
\[ w_{q} =\frac{4\cdot q\cdot a^{4}}{\pi^{5}\cdot D}\cdot \sum\limits_{m=1}^\infty {\left\{ {\frac{1}{m^{5}}\cdot \left[ {1-\frac{\frac{m\cdot \pi \cdot b}{2\cdot a}\cdot th\left( {\frac{m\cdot \pi \cdot b}{2\cdot a}} \right)+2}{2\cdot ch\left( {\frac{m\cdot \pi \cdot b}{2\cdot a}} \right)}} \right]\cdot \sin \left( {\frac{m\cdot \pi }{2}} \right)} \right\}} ; \] \[ w_{P} =\frac{P\cdot a^{2}}{2\cdot \pi^{3}\cdot D}\cdot \sum\limits_{m=1}^\infty {\left\{ {\frac{1}{m^{3}}\cdot \left[ {th\left( {\frac{m\cdot \pi \cdot b}{2\cdot a}} \right)-\frac{\frac{m\cdot \pi \cdot b}{2\cdot a}}{ch^{2}\left( {\frac{m\cdot \pi \cdot b}{2\cdot a}} \right)}} \right]\cdot \sin^{2}\left( {\frac{m\cdot \pi }{2}} \right)} \right\}} , \quad where: \quad \] \[ D=\frac{E\cdot h^{3}}{12\cdot \left( {1-\nu^{2}} \right)}. \]
