Doubly Clamped Beam Subjected to a Uniformly Distributed Load, Concentrated Longitudinal and Shear Forces and a Bending Moment
Objective: Determination of the stress-strain state of a doubly clamped beam subjected to a uniformly distributed load, concentrated longitudinal and shear forces and a bending moment.
Initial data file: SSLL01_v11.3.spr
Problem formulation: The doubly clamped beam is subjected to a load P uniformly distributed over the entire length of the span l, unidirectional concentrated longitudinal forces F1 and F2, applied at the distance of 0.3l from the left and right end respectively, concentrated shear force F, applied at the distance of 0.3l from the right end, and a concentrated bending moment C, applied at the distance of 0.3l from the left end. Determine the vertical displacement Z, longitudinal force N and bending moment M in the middle of the beam span (point G), and the horizontal reaction at the left end of the beam H (point A).
References: S. Timoshenko, Resistance des materiaux, t.1, Paris, Eyrolles, 1976, p. 26. M. Courtand et P. Lebelle, Formulaire du beton arme, t.2, Paris, Eyrolles, 1976, p. 219.
Initial data:
| E = 2.0·1011 Pa | - elastic modulus, |
| μ = 0.2 | - Poisson’s ratio, |
| l = 1.0 m | - beam length; |
| J = 1.7·10-8 m4 | - cross-sectional moment of inertia cross-sectional moment of inertia; |
| P = 24000 N/m | - value of the uniformly distributed load; |
| F1 = 30000 N | - value of the concentrated longitudinal force; |
| F2 = 10000 N | - value of the concentrated longitudinal force; |
| F = 20000 N | - value of the concentrated shear force; |
| C = 24000 N·m | - value of the concentrated bending moment. |
Finite element model: Design model – general type system, 4 bar elements of type 10. Boundary conditions at the clamped ends are provided by imposing constraints in the directions of the degrees of freedom: X, Y, Z, UX, UY, UZ. Number of nodes in the design model – 5.
Results in SCAD
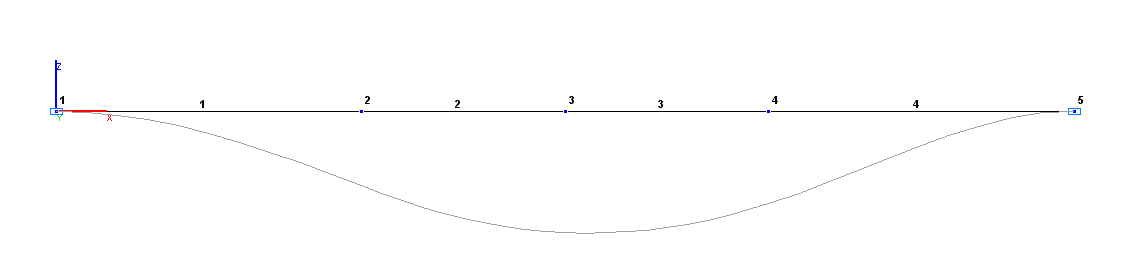
Design and deformed models
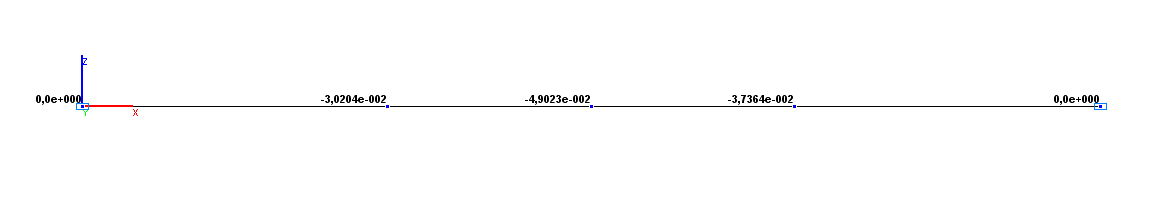
Values of vertical displacements Z (m)
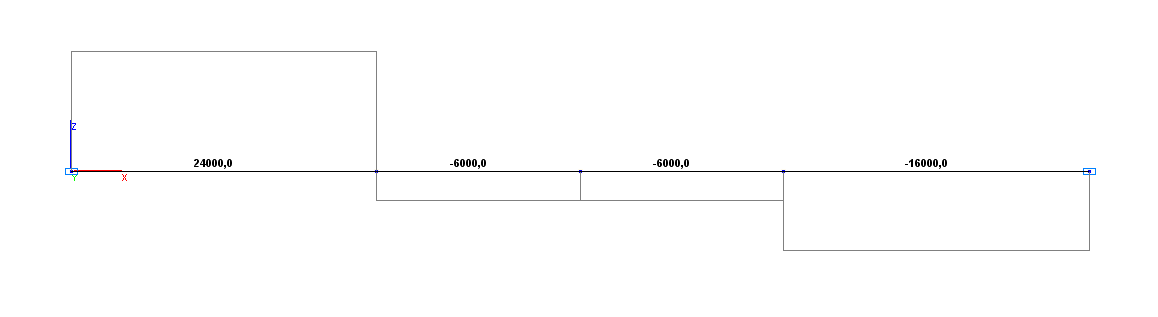
Longitudinal force diagram N (N)
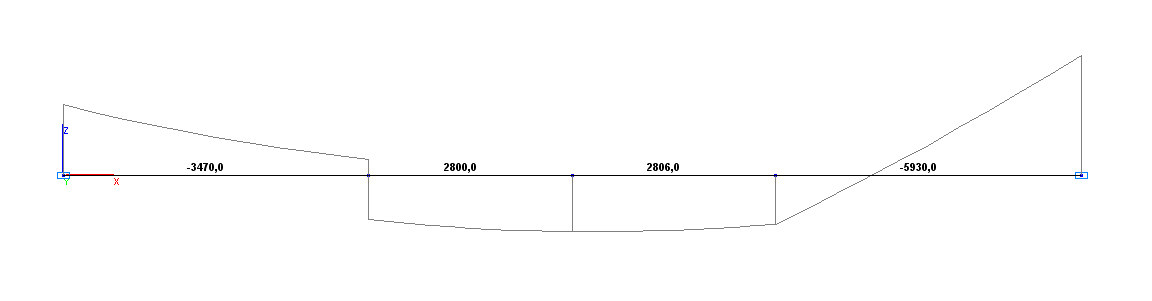
Bending moment diagram М (kN*m)
Comparison of solutions:
|
Parameter |
Theory |
SCAD |
Deviations, % |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Vertical displacement Z (point G), m |
-4.9023·10-2 |
-4.9000·10-2 |
0.05 |
|
Longitudinal force N (point G), N |
-6000.0 |
-6000.0 |
0.00 |
|
Bending moment M (point G), N·m |
2800.0 |
2800.0 |
0.00 |
|
Horizontal reaction H (point A), N |
24000.0 |
24000.0 |
0.00 |
