Plane Frame Subjected to a Uniformly Distributed Instantaneous Pulse
Objective: Determination of the stress-strain state of a plane frame subjected to a uniformly distributed instantaneous pulse.
Initial data file: DI_F.SPR
Problem formulation: The three-storey single-span plane frame with clamped columns and mass uniformly distributed over the columns m1 and girders m2 is subjected to an instantaneous pulse s uniformly distributed along the contour of the first storey. Determine the amplitude values of the bending moment M in the girder of the first storey in the section of its connection with the left column taking into account the following assumption made when deriving the analytical solution: it is assumed that there are no linear displacements of the beam-to-column joints when the symmetric design model is subjected to a symmetric loading and the longitudinal deformations of the frame structural members are neglected.
References: Rabinovich I.M., Sinitsyn A.P., Luzhin O.V., Terenin V.M., Analysis of Structures Subject to Pulse Actions, Moscow, Stroyizdat, 1970, p. 91;
Korenev B.G., Rabinovich I.M., Dynamic Analysis of Buildings and Structures (Designer's handbook), Moscow, Stroyizdat, 1984, p. 79.
Initial data:
| E = 2.1·107 tf/m2 | - elastic modulus; |
| h = 6.0 м | - height of the frame columns; |
| I1 = 1·10-4 m4 | - cross-sectional moment of inertia of the frame columns; |
| F1 = 2·10-1 m2 | - cross-sectional area of the frame columns; |
| m1 = 0.0204 tf·s2/m2 | - value of the mass uniformly distributed over the frame columns; |
| l = 5.0 m | - length of the span of the frame girders; |
| I2 = 2·10-4 m4 | - cross-sectional moment of inertia of the frame girders; |
| F2 = 4·10-1 m2 | - cross-sectional area of the frame girders; |
| m2 = 0.0510 tf·s2/m2 | - value of the mass uniformly distributed over the frame girders; |
| s = 0.3· tf∙s/m | - value of the uniformly distributed instantaneous pulse; |
| g = 9.81 m/s2 | - gravitational acceleration. |
Finite element model: Design model – plane frame, 102 bar elements of type 2.
The spacing of the finite element mesh along the longitudinal axes of the columns and girders of the frame is 0.5 m. Boundary conditions of the support nodes of the columns of the first storey are provided by imposing constraints in the directions of the following degrees of freedom: X, Z, UY. Boundary conditions of the beam-to-column joints according to the assumption made when deriving the analytical solution are provided by imposing constraints in the directions of the following degrees of freedom: X, Z. Boundary conditions of the nodes in the center of the girder spans according to the assumption made when deriving the analytical solution are provided by imposing constraints in the directions of the following degrees of freedom: X, UY. The distributed mass is specified by transforming the static load on the columns m1·g and on the girders m2·g of the frame. The action of the distributed instantaneous pulse is reduced to a number of nodal actions with the values 0.5·s. Number of nodes in the design model – 101. The determination of the natural oscillation modes and natural frequencies is performed by the method of subspace iteration. The matrix of concentrated masses is used in the calculation.
Results in SCAD:
Design model
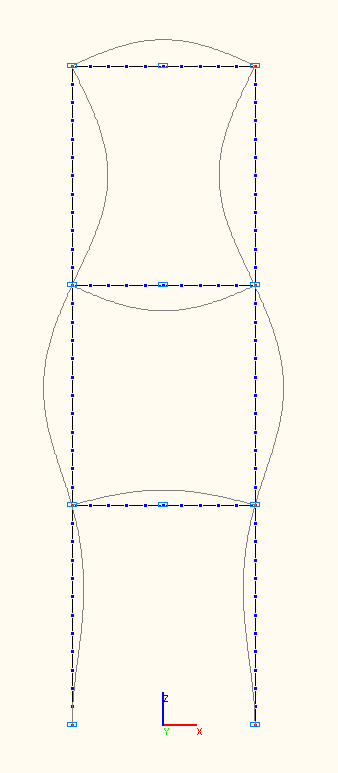
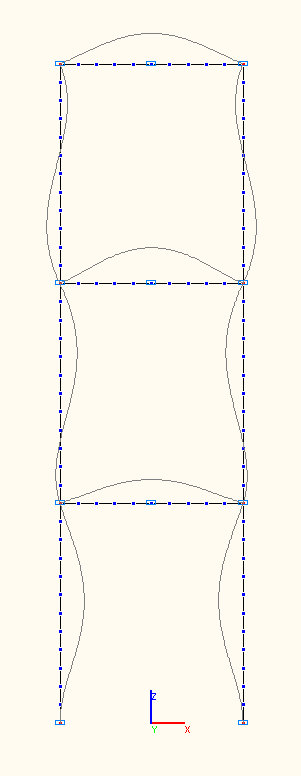
1-st, 2-nd, 3-rd natural oscillation modes
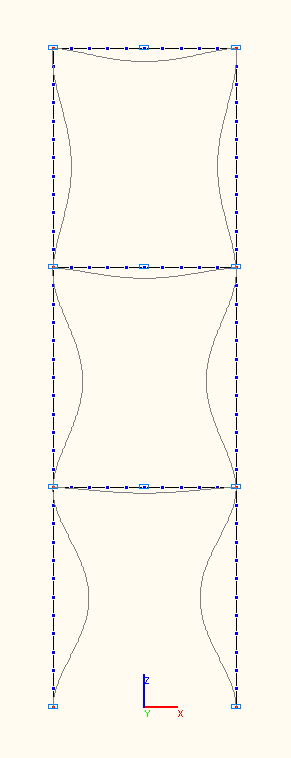
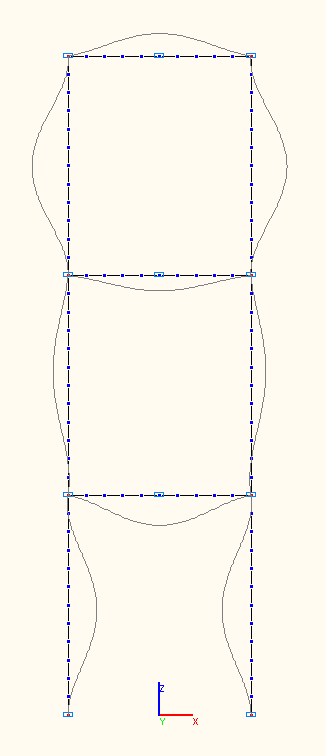
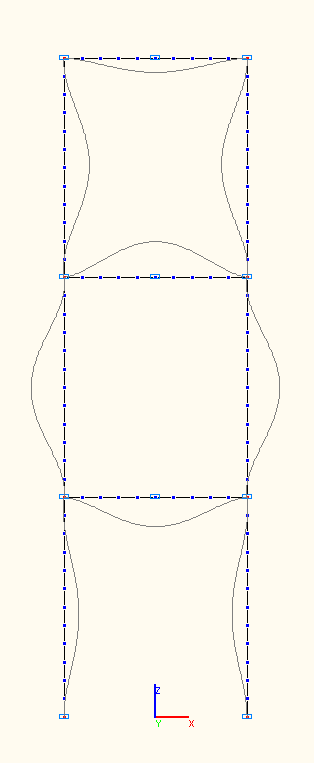
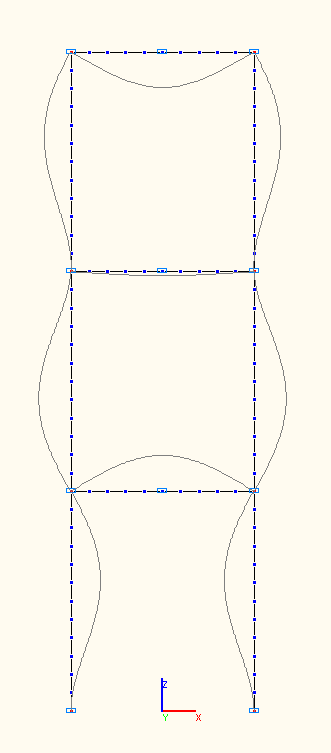
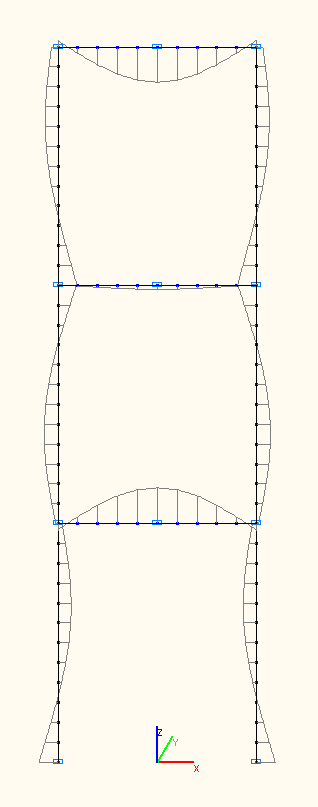
7-th, 8-th, 9-th natural oscillation modes
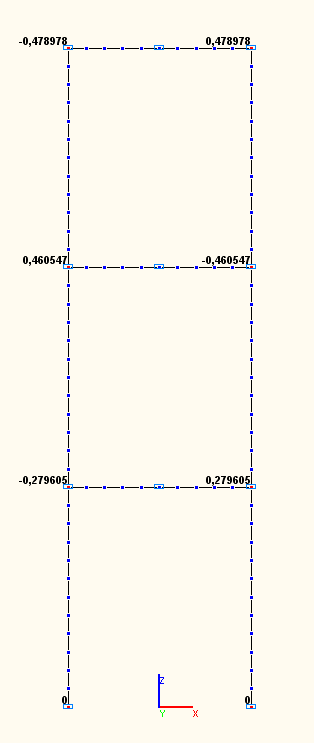
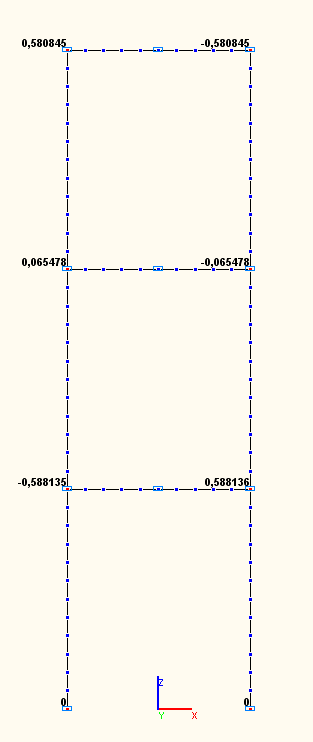
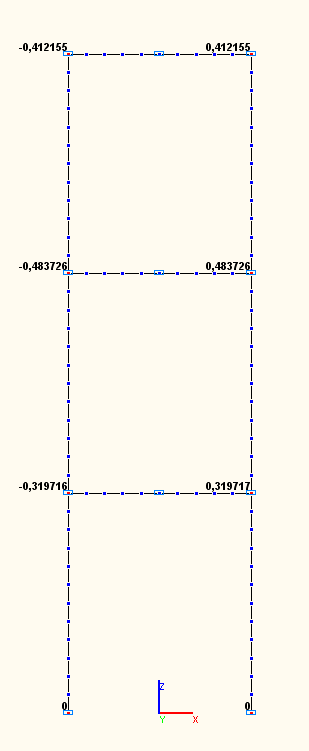
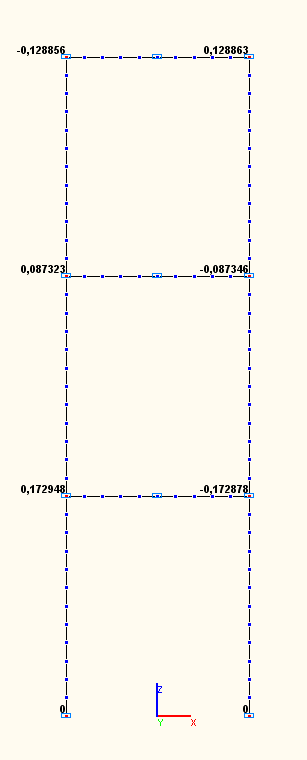
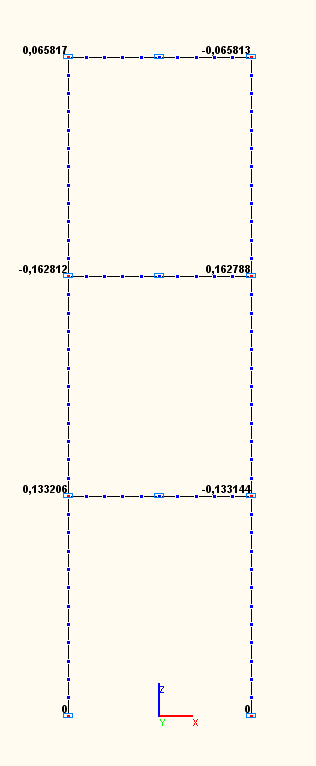
Amplitude values of the angular displacements UYij (rad) in the beam-to-column joints according to the 1-st, 2-nd, 3-rd natural oscillation modes (modal analysis)
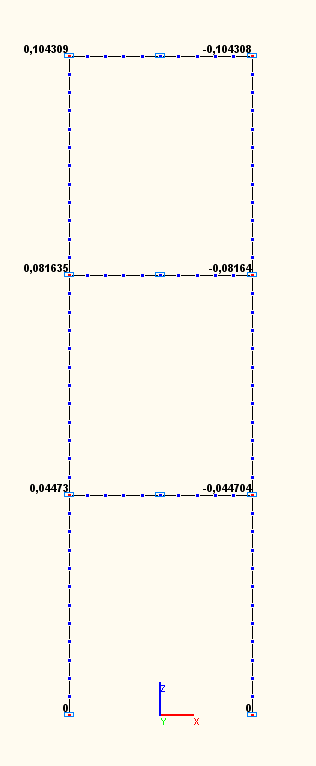
Amplitude values of the angular displacements UYij (rad) in the beam-to-column joints according to the 7-th, 8-th, 9-th natural oscillation modes (modal analysis)
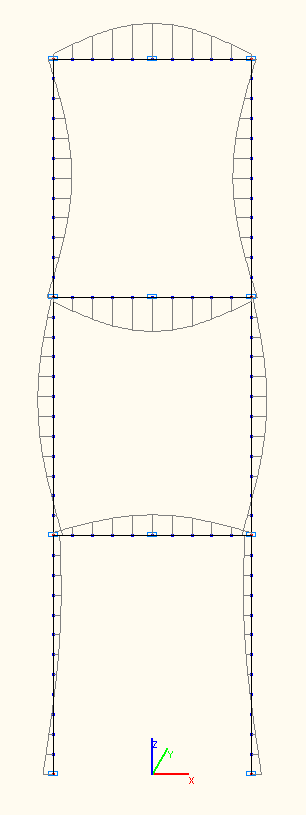
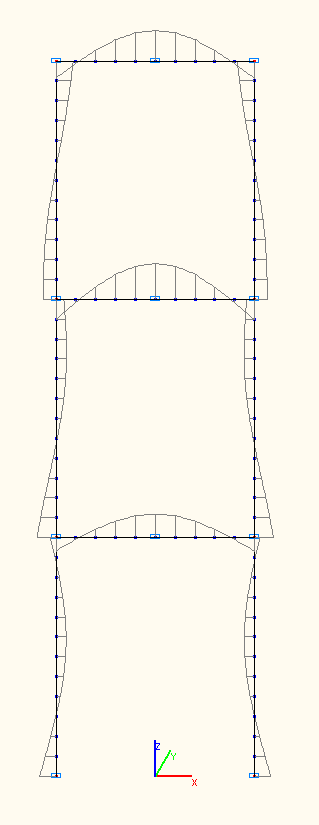
Bending moment diagrams at the amplitude values Mi (tf·m) according to the 1-st, 2-nd, 3-rd natural oscillation modes
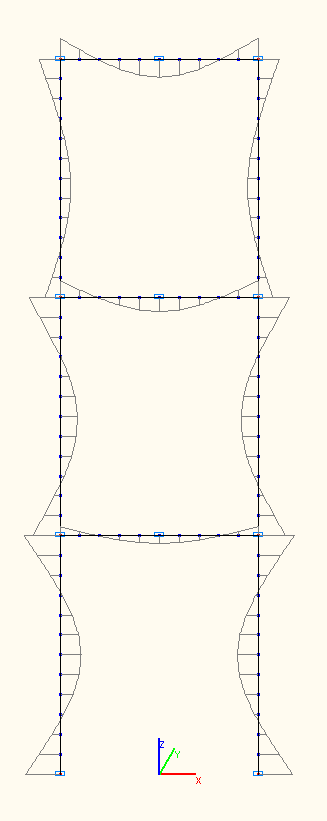
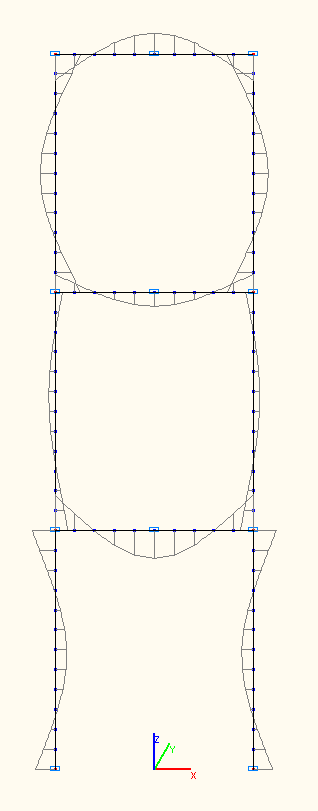
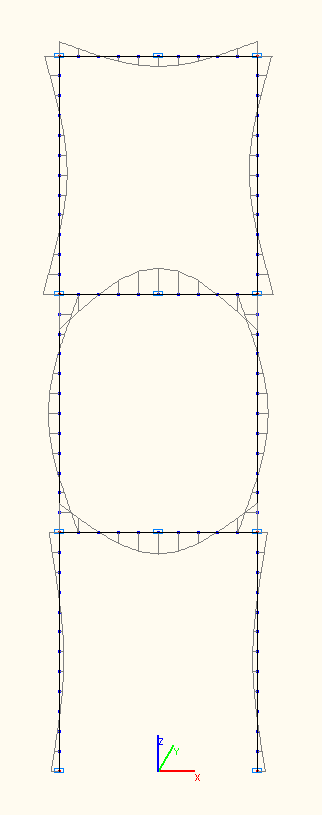
Bending moment diagrams at the amplitude values Mi (tf·m) according to the 7-th, 8-th, 9-th natural oscillation modes
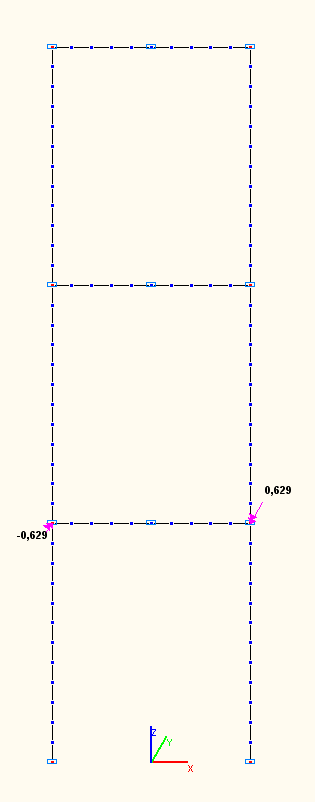
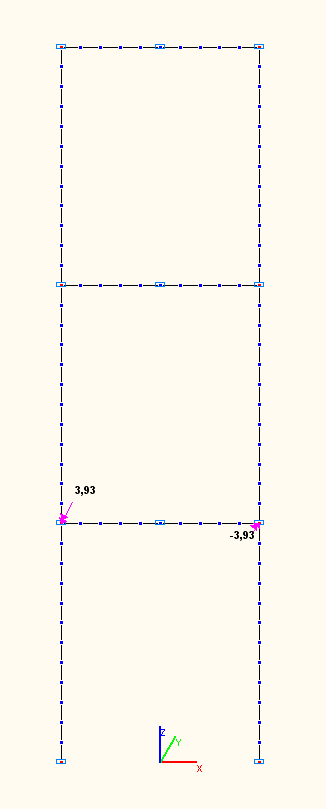
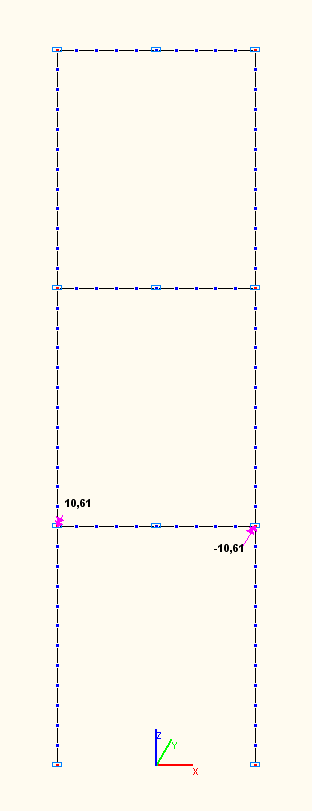
Amplitude values of the bending moments Mi (tf·m) in the girder of the first floor in the sections of its connections with the columns according to the 1-st, 2-nd, 3-rd natural oscillation modes
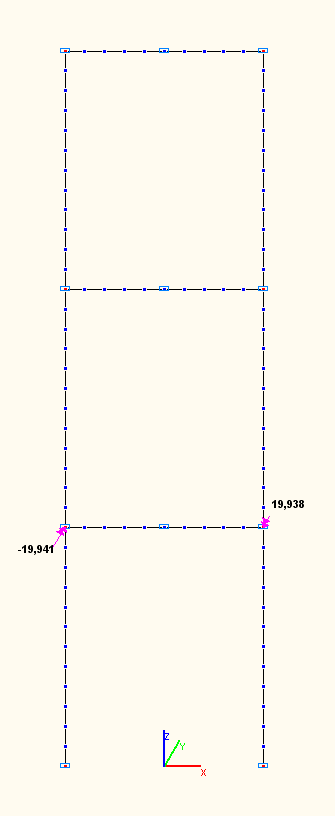
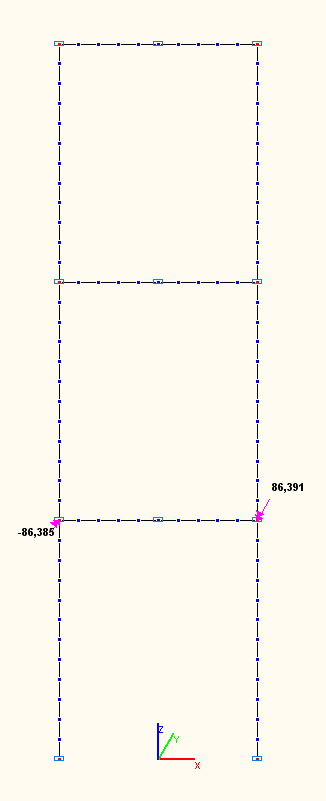
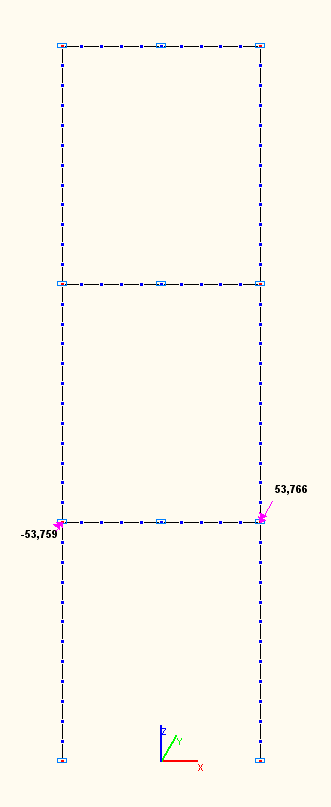
Amplitude values of the bending moments Mi (tf·m) in the girder of the first floor in the sections of its connections with the columns according to the 7-th, 8-th, 9-th natural oscillation modes
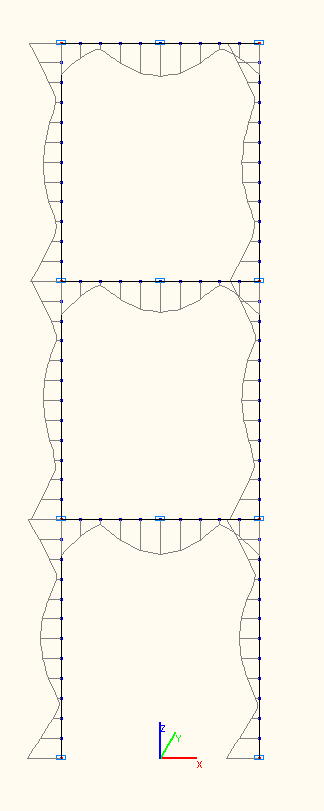
Bending moment diagram at the amplitude values M (tf·m) from the total pulse load
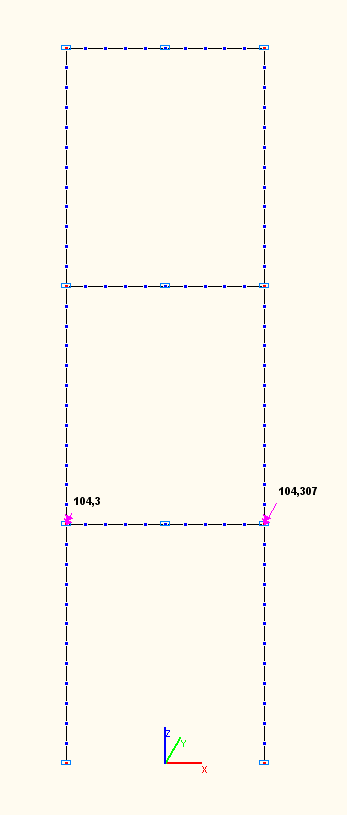
Amplitude values of the bending moments M (tf·m) in the girder of the first floor in the sections of its connections with the columns from the total pulse load
Comparison of solutions:
Natural periods T, s
|
Oscillation mode |
Theory |
SCAD |
Deviations, % |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
0.060607 |
0.060607 |
0.00 |
|
2 |
0.049785 |
0.049785 |
0.00 |
|
3 |
0.040435 |
0.040436 |
0.00 |
|
7 |
0.030924 |
0.030925 |
0.00 |
|
8 |
0.028903 |
0.028904 |
0.00 |
|
9 |
0.027787 |
0.027788 |
0.00 |
Amplitude values of the angular displacements UYij (rad) in the beam-to-column joints according to the 1-st, 2-nd, 3-rd, 7-th, 8-th, 9-th natural oscillation modes (modal analysis)
|
Oscillation mode |
Storey |
Theory |
SCAD |
Deviation, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
1 |
+0.583753 |
-0.279605 / -0.478978 = = +0.583753 |
0.00 |
|
1 |
2 |
-0.961520 |
+0.460547 / -0.478978 = = -0.961520 |
0.00 |
|
1 |
3 |
+1.000000 |
-0.478978 / -0.478978 = = +1.000000 |
0.00 |
|
2 |
1 |
-1.012550 |
-0.588135 / +0.580845 = = -1.012551 |
0.00 |
|
2 |
2 |
+0.112727 |
+0.065478 / +0.580845 = = +0.112729 |
0.00 |
|
2 |
3 |
+1.000000 |
+0.580845 / +0.580845 = = +1.000000 |
0.00 |
|
3 |
1 |
+0.775708 |
-0.319716 / -0.412155 = = +0.775718 |
0.00 |
|
3 |
2 |
+1.173640 |
-0.483726 / -0.412155 = = +1.173651 |
0.00 |
|
3 |
3 |
+1.000000 |
-0.412155 / -0.412155 = = +1.000000 |
0.00 |
|
7 |
1 |
+0.428722 |
+0.044730 / +0.104309 = = +0.428822 |
0.00 |
|
7 |
2 |
+0.782640 |
+0.081635 / +0.104309 = = +0.782627 |
0.00 |
|
7 |
3 |
+1.000000 |
+0.044730 / +0.104309 = = +1.000000 |
0.00 |
|
8 |
1 |
-1.342142 |
+0.172948 / -0.128856 = = -1.342180 |
0.00 |
|
8 |
2 |
-0,677645 |
+0.087323 / -0.128856 = = -0,677679 |
0.00 |
|
8 |
3 |
+1.000000 |
-0.128856 / -0.128856 = = +1.000000 |
0.00 |
|
9 |
1 |
+2.023786 |
+0.133206 / +0.065817 = = +2.023884 |
0.00 |
|
9 |
2 |
-2.473762 |
-0.162812 / +0.065817 = = -2.473707 |
0.00 |
|
9 |
3 |
+1.000000 |
+0.065817 / +0.065817 = = +1.000000 |
0.00 |
Amplitude values of the bending moments Mi (tf·m) in the girder of the first floor in the section of its connection with the left column according to the 1-st, 2-nd, 3-rd, 7-th, 8-th, 9-th natural oscillation modes
|
Oscillation mode |
Theory |
SCAD |
Deviations, % |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
+0.629 |
-0.629 |
0.00 |
|
2 |
-3.931 |
+3.930 |
0.03 |
|
3 |
-10.611 |
+10.610 |
0.01 |
|
7 |
+19.939 |
-19.941 |
0.01 |
|
8 |
+86.385 |
-86.385 |
0.00 |
|
9 |
+53.755 |
-53.759 |
0.01 |
|
Parameter |
Theory |
SCAD |
Deviations, % |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Amplitude values of the bending moment M in the girder of the first floor in the section of its connection with the left column from the total pulse load, tf·m |
+165.576 (+173.075) |
+175.241 |
5.84 (1.25) |
The theoretical value of the bending moment in the girder corresponds to the time point t = 0.036 s from the start of the action of the pulse load;
The theoretical value of the bending moment in the girder given in the brackets was determined taking into account the phase shift of the harmonics.
Notes: In the analytical solution the natural periods T, amplitude values of the angular displacements UYij in the beam-to-column joints at the modal analysis, amplitude values of the bending moments in the girder of the first storey in the section of its connection with the left column according to the natural oscillation modes Mi and from the total pulse load M are determined according to the following formulas:
\[ T_{i} =\frac{2\cdot \pi }{\omega_{i} }; \quad \omega_{i} =\frac{\lambda_{i}^{2}}{h^{2}}\cdot \sqrt {\frac{E\cdot I_{1} }{m_{1} }} ; \]
λi – are determined from the following expression:
\[ \left\{ 4\cdot \left[ {ch( \lambda )\cdot \sin ( \lambda )-sh( \lambda)\cdot \cos ( \lambda )} \right]^{3}-3\cdot \left[ {sh( \lambda)-\sin ( \lambda)} \right]^{2}\cdot \left[ {ch( \lambda)\cdot \sin ( \lambda)-sh( \lambda )\cdot \cos ( \lambda )} \right] \right\} / {\left[ {1-ch( \lambda)\cdot \cos( \lambda)} \right]^{3}}+ \] \[ +\beta^{2}\cdot \alpha^{2}\cdot \left\{ {5\cdot \left[ {ch( \lambda )\cdot \sin ( \lambda )-sh( \lambda )\cdot \cos ( \lambda )} \right]\cdot \left[ {ch( {\alpha \cdot \lambda } )\cdot \sin ( {\alpha \cdot \lambda } )-sh( {\alpha \cdot \lambda } )\cdot \cos ( {\alpha \cdot \lambda } } \right]^{2}} \right.+ \] \[ +5\cdot \left[ {sh\left( {\alpha \cdot \lambda } \right)-\sin \left( {\alpha \cdot \lambda } \right)} \right]^{2}\cdot \left[ {ch\left( \lambda \right)\cdot \sin \left( \lambda \right)-sh\left( \lambda \right)\cdot \cos \left( \lambda \right)} \right]- \] \[ \left. -10\cdot \left[ sh( {\alpha \cdot \lambda } )-\sin ( {\alpha \cdot \lambda } ) \right]\cdot \left[ ch( \lambda )\cdot \sin ( \lambda )-sh( \lambda )\cdot \cos ( \lambda ) \right]\cdot \left[ ch( {\alpha \cdot \lambda } )\cdot \sin ( {\alpha \cdot \lambda } )-sh( {\alpha \cdot \lambda } )\cdot \cos ( {\alpha \cdot \lambda } ) \right] \right\} / \] \[ / \left\{ \left[ {1-ch( \lambda )\cdot \cos ( \lambda )} \right]\cdot \left[ 1-ch( {\alpha \cdot \lambda )\cdot \cos ( \alpha \cdot \lambda )} \right]^{2} \right\}+ \] \[ +\beta\cdot \alpha\cdot \left\{ {8\cdot \left[ {ch( \lambda )\cdot \sin ( \lambda )-sh( \lambda )\cdot \cos ( \lambda )} \right]^2\cdot \left[ {ch( {\alpha \cdot \lambda } )\cdot \sin ( {\alpha \cdot \lambda } )-sh( {\alpha \cdot \lambda } )\cdot \cos ( {\alpha \cdot \lambda } } \right]} \right.- \] \[ -8\cdot \left[ {sh\left( {\alpha \cdot \lambda } \right)-\sin \left( {\alpha \cdot \lambda } \right)} \right]\cdot \left[ {ch\left( \lambda \right)\cdot \sin \left( \lambda \right)-sh\left( \lambda \right)\cdot \cos \left( \lambda \right)} \right]^{2}- \] \[ \left. -2\cdot \left[ sh( \lambda )-\sin ( \lambda ) \right]^{2}\cdot \left[ ch( {\alpha \cdot \lambda } )\cdot \sin ( {\alpha \cdot \lambda } )-sh( {\alpha \cdot \lambda } )\cdot \cos ( {\alpha \cdot \lambda } ) \right]+2\cdot \left[ sh( \lambda )-\sin ( \lambda ) \right]^{2}\cdot \left[ sh( {\alpha \cdot \lambda } )-\sin (\alpha \cdot \lambda) \right] \right\} / \] \[ / \left\{ \left[ {1-ch( \lambda )\cdot \cos ( \lambda )} \right]^{2}\cdot \left[ 1-ch( {\alpha \cdot \lambda )\cdot \cos ( \alpha \cdot \lambda )} \right] \right\}+ \] \[ + \beta^{3}\cdot \alpha^{3}\cdot \left\{ \left[ ch( \alpha \cdot \lambda )\cdot \sin( \alpha \cdot \lambda )-sh( \alpha \cdot \lambda)\cdot \cos ( \alpha \cdot \lambda ) \right]^{3} +3\cdot \left[ sh( \alpha \cdot \lambda )-\sin (\alpha \cdot \lambda) \right]^{2}\cdot \left[ ch(\alpha \cdot \lambda)\cdot \sin (\alpha \cdot \lambda)-sh( \alpha \cdot \lambda )\cdot \cos (\alpha \cdot \lambda) \right]- \right. \] \[ \left. -3\cdot \left[ {sh(\alpha \cdot \lambda)-\sin (\alpha \cdot \lambda)} \right]\cdot \left[ ch( {\alpha \cdot \lambda } )\cdot \sin (\alpha \cdot \lambda )-sh(\alpha \cdot \lambda)\cdot \cos (\alpha \cdot \lambda) \right]^{2}-\left[ {sh(\alpha \cdot \lambda } )-\sin (\alpha \cdot \lambda) \right]^{3} \right\} / \] \[ / \left\{ \left[ 1-ch( \alpha \cdot \lambda)\cdot \cos (\alpha \cdot \lambda ) \right]^{3} \right\} = 0, \quad where: \] \[ \alpha =\frac{l}{h}\cdot \sqrt[4]{\frac{m_{2} \cdot I_{1} }{m_{1} \cdot I_{2} }}, \quad \beta =\frac{h}{l}\cdot \frac{I_{2} }{I_{1} }; \] \[ UY_{i1} =\left\{ \left[ ch(\lambda_{i} )\cdot \sin (\lambda_{i})-sh(\lambda_{i})\cdot \cos (\lambda_{i}) \right] \cdot \left[ 1-ch(\alpha \cdot \lambda_{i})\cdot \cos (\alpha \cdot \lambda)_{i} \right]+ \right. \] \[ \left. +\beta \cdot \alpha \cdot \left[ \sin (\alpha \cdot \lambda_{i})\cdot \left[ ch(\alpha \cdot \lambda_{i})+1 \right] -sh( \alpha \cdot \lambda_{i})\cdot \left[ \cos (\alpha \cdot \lambda_{i})+1 \right] \right] \cdot \left[ 1-ch (\lambda_{i} )\cdot \cos ( \lambda )_{i} \right] \right\} \cdot UY_{i3} / \] \[ / \left\{ 2\cdot \left[ ch( \lambda_{i})\cdot \sin (\lambda_{i}) -sh ( \lambda_{i})\cdot \cos (\lambda_{i}) \right] \cdot \left[ 1-ch (\alpha \cdot \lambda_{i})\cdot \cos (\alpha \cdot \lambda)_{i} \right] + \right. \] \[ \left. +\beta \cdot \alpha \cdot \left[ \sin (\alpha \cdot \lambda_{i})\cdot \left[ ch(\alpha \cdot \lambda_{i})+1 \right] -sh( \alpha \cdot \lambda_{i})\cdot \left[ \cos (\alpha \cdot \lambda_{i})+1 \right] \right] \cdot \left[ 1-ch (\lambda_{i} )\cdot \cos ( \lambda )_{i} \right] \right\} , \] \[ UY_{i2} =\left\{ \left[ ch(\lambda_{i} )\cdot \sin (\lambda_{i})-sh(\lambda_{i})\cdot \cos (\lambda_{i}) \right] \cdot \left[ 1-ch(\alpha \cdot \lambda_{i})\cdot \cos (\alpha \cdot \lambda)_{i} \right]+ \right. \] \[ \left. +\beta \cdot \alpha \cdot \left[ \sin (\alpha \cdot \lambda_{i})\cdot \left[ ch(\alpha \cdot \lambda_{i})+1 \right] -sh( \alpha \cdot \lambda_{i})\cdot \left[ \cos (\alpha \cdot \lambda_{i})+1 \right] \right] \cdot \left[ 1-ch (\lambda_{i} )\cdot \cos ( \lambda )_{i} \right] \right\} \cdot UY_{i3} / \] \[ / \left\{ \cdot \left[ ch( \lambda_{i})\cdot \sin (\lambda_{i}) \right] \cdot \left[ 1-ch (\alpha \cdot \lambda_{i})\cdot \cos (\alpha \cdot \lambda)_{i} \right] + \right\}, \] \[ UY_{i3} =1.0; \]
\( M=\sum\limits_{i=1}^N {M_{i} \cdot \sin \left( {\omega_{i} \cdot t} \right)} \) - without taking into account the phase shift of the harmonics,
t - are determined from the following expression:
\[ \sum\limits_{i=1}^N {\omega_{i} \cdot M_{i} \cdot \cos \left( {\omega_{i} \cdot t} \right)} =0, \]
\( M=\sum\limits_{i=1}^{q-1} {\left| {M_{i} } \right|\cdot \sin \left( {\frac{\pi \cdot \omega_{i} }{2\cdot \omega_{q} }} \right)+} \sum\limits_{i=q}^N {\left| {M_{i} } \right|}, \quad at \quad \left| {M_{q} } \right|>\left| {M_{i} } \right|\quad, \quad\left( {i\ne q} \right) \) - taking into account the phase shift of the harmonics, where: \[ M_{i} =A_{i} \cdot M_{gi} , \quad A_{i} =\frac{A_{i1} }{A_{i2} \cdot \omega_{i} }, \] \[ A_{i1} =\frac{2\cdot s\cdot UY_{i1} }{\lambda_{i}^{2}}\cdot \left\{ {h^{2}\cdot \frac{ch\left( {\lambda_{i} } \right)-\cos \left( {\lambda_{i} } \right)-sh\left( {\lambda_{i} } \right)\cdot \sin \left( {\lambda_{i} } \right)}{1-ch\left( {\lambda_{i} } \right)\cdot \cos \left( {\lambda_{i} } \right)}-\frac{l^{2}}{\alpha^{2}}\cdot \frac{ch\left( {\alpha \cdot \lambda _{i} } \right)-\cos \left( {\alpha \cdot \lambda_{i} } \right)-sh\left( {\alpha \cdot \lambda_{i} } \right)\cdot \sin \left( {\alpha \cdot \lambda _{i} } \right)}{1-ch\left( {\alpha \cdot \lambda_{i} } \right)\cdot \cos \left( {\alpha \cdot \lambda_{i} } \right)}} \right\}, \] \[ A_{i2} =\frac{m_{1} \cdot h^{3}}{\lambda_{i}^{3}}\cdot \left\{ {\left( {UY_{i1}^{2}+UY_{i2}^{2}+\frac{UY_{i3}^{2}}{2}} \right)} \right.\cdot \left[ {\lambda_{i} \cdot \frac{\left[ {sh\left( {\lambda_{i} } \right)-\sin \left( {\lambda_{i} } \right)} \right]^{2}}{\left[ {1-ch\left( {\lambda_{i} } \right)\cdot \cos \left( {\lambda_{i} } \right)} \right]^{2}}-\frac{ch\left( {\lambda_{i} } \right)\cdot \sin \left( {\lambda_{i} } \right)-sh\left( {\lambda_{i} } \right)\cdot \cos \left( {\lambda_{i} } \right)}{1-ch\left( {\lambda_{i} } \right)\cdot \cos \left( {\lambda_{i} } \right)}} \right]+ \] \[ \left. {\left( {UY_{i1} \cdot UY_{i2} +UY_{i2} \cdot UY_{i3} } \right)\cdot \left[ {\lambda_{i} \cdot \frac{\left[ {sh\left( {\lambda_{i} } \right)-\sin \left( {\lambda_{i} } \right)} \right]\cdot \left[ {ch\left( {\lambda_{i} } \right)\cdot \sin \left( {\lambda_{i} } \right)-sh\left( {\lambda_{i} } \right)\cdot \cos \left( {\lambda_{i} } \right)} \right]}{\left[ {1-ch\left( {\lambda_{i} } \right)\cdot \cos \left( {\lambda_{i} } \right)} \right]^{2}}-\lambda_{i} \cdot \frac{ch\left( {\lambda_{i} } \right)-\cos \left( {\lambda_{i} } \right)}{1-ch\left( {\lambda_{i} } \right)\cdot \cos \left( {\lambda_{i} } \right)}-\frac{sh\left( {\lambda_{i} } \right)-\sin \left( {\lambda_{i} } \right)}{1-ch\left( {\lambda_{i} } \right)\cdot \cos \left( {\lambda_{i} } \right)}} \right]} \right\} + \] \[ \frac{m_2\cdot l^3}{2\cdot\alpha^3\lambda_i^3} \left\{ \left(UY_{i1}^2+UY_{i2}^2+UY_{i3}^2 \right)\cdot \left[ \alpha\cdot\lambda_i \frac{\left[sh(\alpha\cdot\lambda_i)-\sin(\alpha\cdot\lambda_i)\right]^2}{\left[1-ch(\alpha\cdot\lambda_i)\cdot\cos(\alpha\cdot\lambda_i)\right]^2} -\frac{ch(\alpha\cdot\lambda_i)\cdot\sin(\alpha\cdot\lambda_i)-sh(\alpha\cdot\lambda_i)\cdot\cos(\alpha\cdot\lambda_i)}{1-ch(\alpha\cdot\lambda_i)\cdot\cos(\alpha\cdot\lambda_i)}- \right. \right. \] \[ -\alpha \cdot \lambda_{i} \cdot \frac{\left[ {sh\left( {\alpha \cdot \lambda_{i} } \right)-\sin \left( {\alpha \cdot \lambda_{i} } \right)} \right]\cdot \left[ {ch\left( {\alpha \cdot \lambda_{i} } \right)\cdot \sin \left( {\alpha \cdot \lambda_{i} } \right)-sh\left( {\alpha \cdot \lambda _{i} } \right)\cdot \cos \left( {\alpha \cdot \lambda_{i} } \right)} \right]}{\left[ {1-ch\left( {\alpha \cdot \lambda_{i} } \right)\cdot \cos \left( {\alpha \cdot \lambda_{i} } \right)} \right]^{2}}+\alpha \cdot \lambda_{i} \cdot \frac{ch\left( {\alpha \cdot \lambda_{i} } \right)-\cos \left( {\alpha \cdot \lambda_{i} } \right)}{1-ch\left( {\alpha \cdot \lambda_{i} } \right)\cdot \cos \left( {\alpha \cdot \lambda_{i} } \right)}+ \] \[ \left. {\left. {+\frac{sh\left( {\alpha \cdot \lambda_{i} } \right)-\sin \left( {\alpha \cdot \lambda_{i} } \right)}{1-ch\left( {\alpha \cdot \lambda_{i} } \right)\cdot \cos \left( {\alpha \cdot \lambda_{i} } \right)}} \right]} \right\} . \] \[ M_{gi} =\frac{E\cdot l_{2} }{l}\cdot \alpha \cdot \lambda_{i} \cdot \frac{\sin \left( {\alpha \cdot \lambda_{i} } \right)\cdot \left( {ch\left( {\alpha \cdot \lambda_{i} } \right)+1} \right)-sh\left( {\alpha \cdot \lambda_{i} } \right)\cdot \left( {\cos \left( {\alpha \cdot \lambda_{i} } \right)+1} \right)}{1-ch\left( {\alpha \cdot \lambda_{i} } \right)\cdot \cos \left( {\alpha \cdot \lambda_{i} } \right)}\cdot UY_{i2} \]
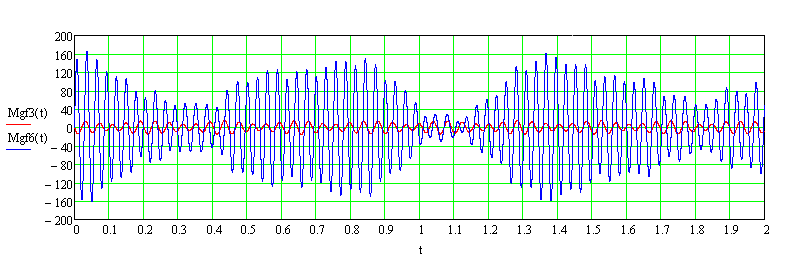
Graph of the variation of the bending moments M (tf·m) with time t (s) in the girder of the first floor in the sections of its connections with the columns from the total pulse load taking into account 3 and 6 symmetric natural oscillation modes
The significant deviation of the results (>5%) in the amplitude values of the bending moment is due to the fact that the summation over the modes in the source Analysis of Structures Subject to Pulse Actions is performed without taking into account the phase shift. Later recommendations contain the requirement to take into account the phase shift. In this case the deviation from the theory is 1.25%.
Dynamic Analysis of Buildings and Structures Dynamic Analysis of Buildings and Structures Analysis of Structures Subject to Pulse Actions Analysis of Structures Subject to Pulse Actions.
