Simply Supported Thick Square Plate Subjected to a Uniformly Distributed Transverse Load
Objective:
Determination of the strain state of a simply supported thick square plate subjected to a uniformly distributed transverse load.
Initial data files:
|
File name |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Design model for the plate side-to-thickness ratios |
|
|
Design model for the plate side-to-thickness ratios |
|
|
Design model for the plate side-to-thickness ratios |
Problem formulation:
The simply supported thick square plate is subjected to a uniformly distributed transverse load p. Determine the deflection w in the center of the plate taking into account the transverse shear deformations.
References: L. G. Donnell, Beam, Plates, and Shells, Moscow, Nauka, 1982, p. 313-316.
Initial data:
| E = 3.0·107 kPa | - elastic modulus, |
| ν = 0.2 | - Poisson’s ratio, |
| h = 2.0; 4.0; 8.0 m | - thickness of the plate; |
| a = 16.0 m | - side of the plate; |
| p = 100.0 kN/m2 | - value of the uniformly distributed transverse load. |
Finite element model:
Three design models for the following plate side-to-thickness ratios a/h = 8.0; 4.0; 2.0 are considered. Four variants of each model with the following types of finite elements are considered: 44, 50 – quadrangular four-node and eight-node thin shell elements for the calculation according to the Kirchhoff-Love theory; 144, 150 – quadrangular four-node and eight-node thick shell elements for the calculation according to the Reissner–Mindlin theory.
Design models are created for the following meshes: 2x2; 4x4; 8x8; 16x16; 32x32; 64x64.
Boundary conditions are provided by imposing constraints in the directions of the degrees of freedom X, Y, Z, UY for the edges along the X axis of the global coordinate system, and X, Y, Z, UX for the edges along the Y axis of the global coordinate system.
Results in SCAD
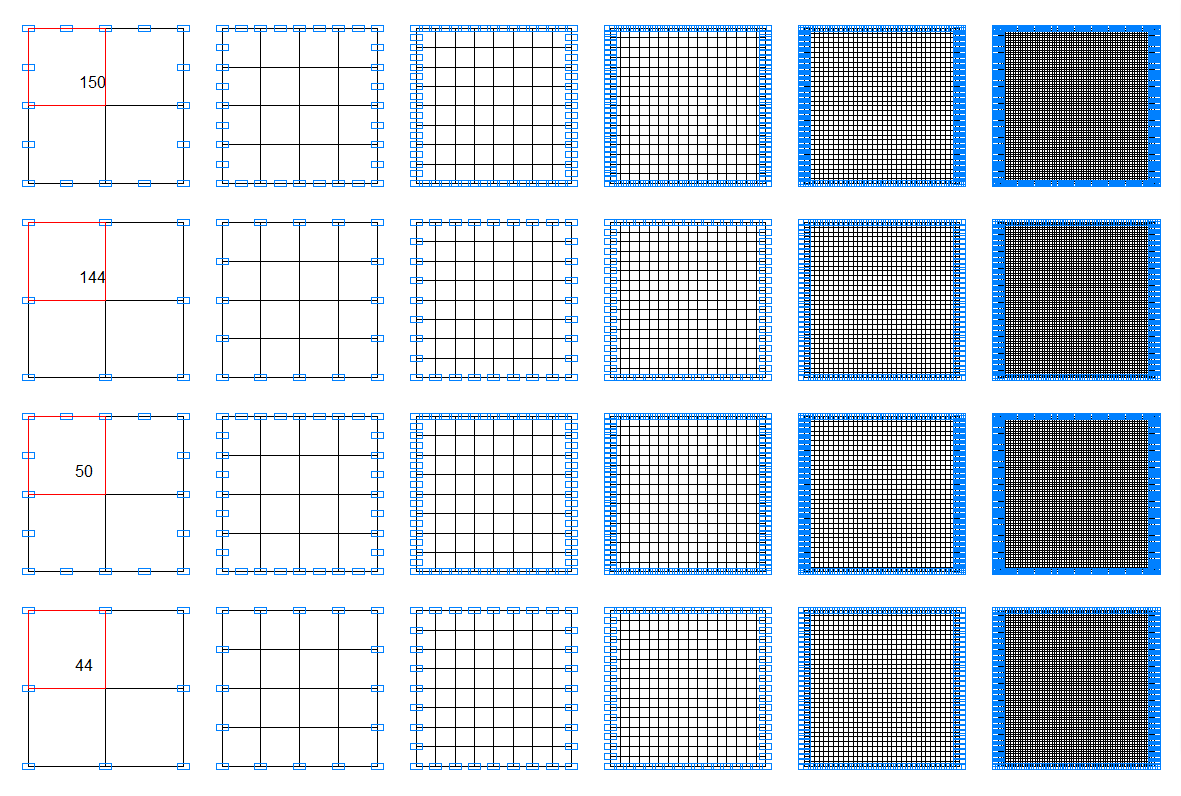

 Design models
Design models
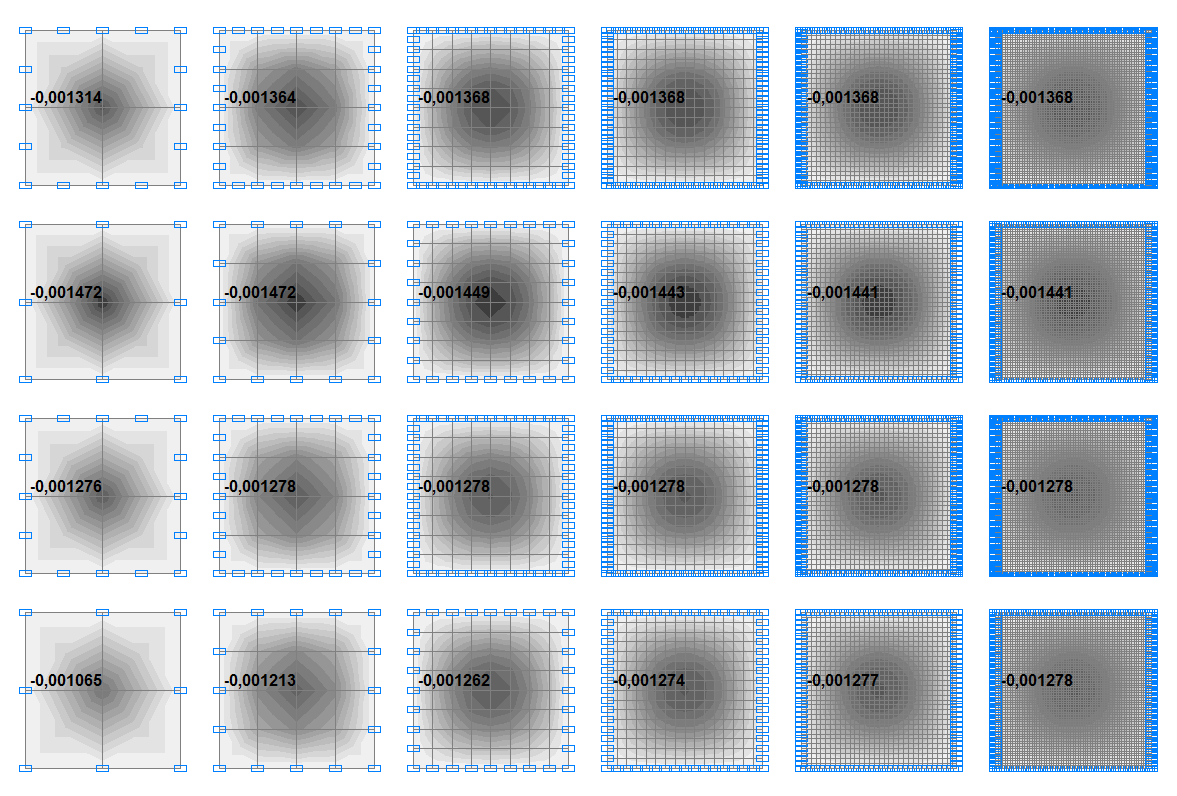
Deflections w of plates with the ratio a/h = 8.0, m
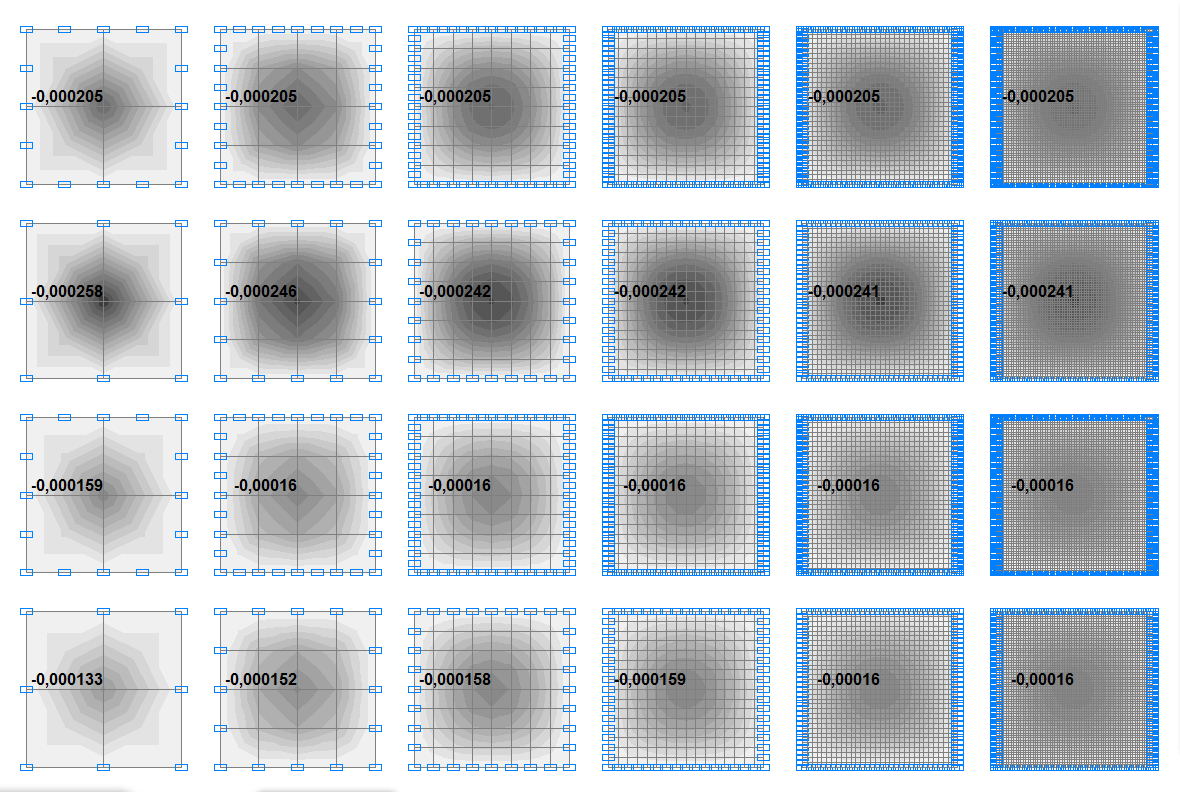
Deflections w of plates with the ratio a/h = 4.0, m
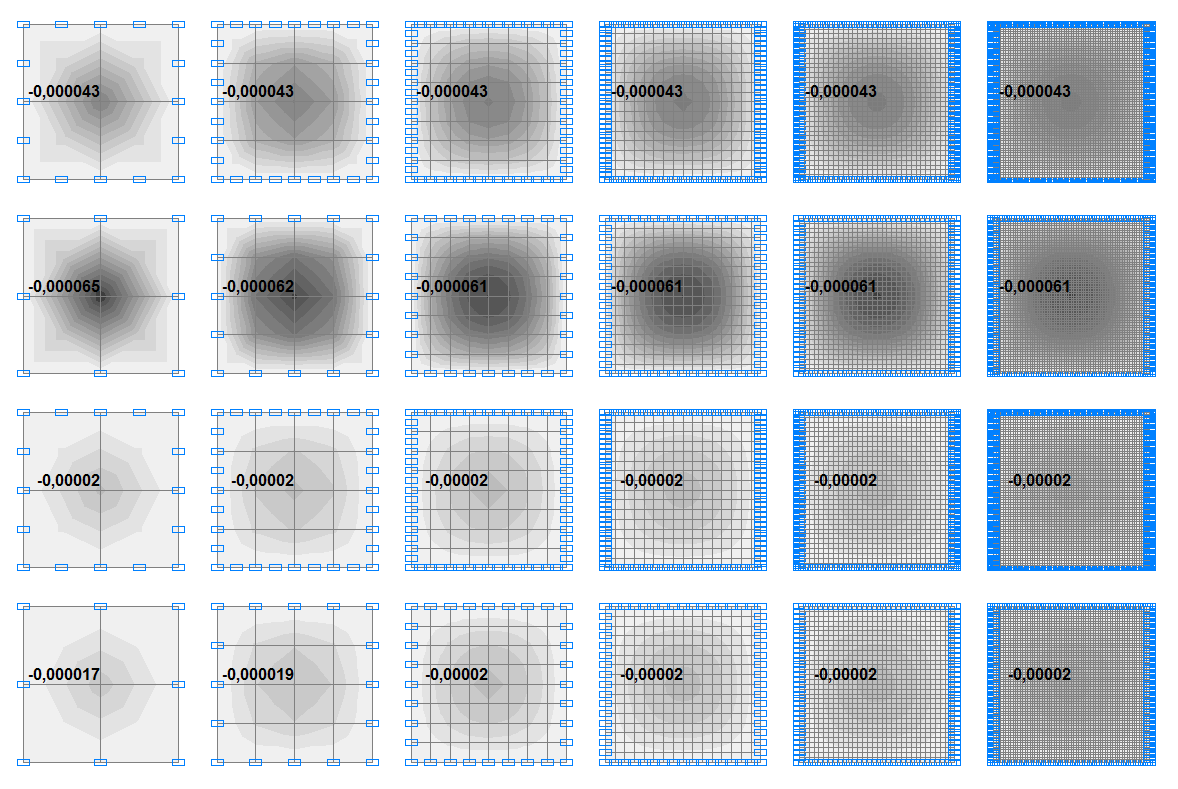
Deflections w of plates with the ratio a/h = 2.0, m
Comparison of solutions:
Deflections w in the center of the plates with the ratio a/h = 8.0, m
|
Member type |
SCAD, mesh |
Theory |
Deviation |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
2x2 |
4x4 |
8x8 |
16x16 |
32x32 |
64x64 |
|||
|
44 |
0.001065 |
0.001213 |
0.001262 |
0.001274 |
0.001277 |
0.001278 |
0.001278 |
0.00 % |
|
50 |
0.001276 |
0.001278 |
0.001278 |
0.001278 |
0.001278 |
0.001278 |
0.00 % |
|
|
144 |
0.001472 |
0.001472 |
0.001449 |
0.001443 |
0.001441 |
0.001441 |
0.001369 |
5.26 % |
|
150 |
0.001314 |
0.001364 |
0.001368 |
0.001368 |
0.001368 |
0.001368 |
0.07 % |
|
Deflections w in the center of the plates with the ratio a/h = 4.0, m
|
Member type |
SCAD, mesh |
Theory |
Deviation |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
2x2 |
4x4 |
8x8 |
16x16 |
32x32 |
64x64 |
|||
|
44 |
0.000133 |
0.000152 |
0.000158 |
0.000159 |
0.000160 |
0.000160 |
0.000160 |
0.00 % |
|
50 |
0.000159 |
0.000160 |
0.000160 |
0.000160 |
0.000160 |
0.000160 |
0.00 % |
|
|
144 |
0.000258 |
0.000246 |
0.000242 |
0.000242 |
0.000241 |
0.000241 |
0.000205 |
17.56 % |
|
150 |
0.000205 |
0.000205 |
0.000205 |
0.000205 |
0.000205 |
0.000205 |
0.00 % |
|
Deflections w in the center of the plates with the ratio a/h = 2.0, m
|
Member type |
SCAD, mesh |
Theory |
Deviation |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
2x2 |
4x4 |
8x8 |
16x16 |
32x32 |
64x64 |
|||
|
44 |
0.000017 |
0.000019 |
0.000020 |
0.000020 |
0.000020 |
0.000020 |
0.000020 |
0.00 % |
|
50 |
0.000020 |
0.000020 |
0.000020 |
0.000020 |
0.000020 |
0.000020 |
0.00 % |
|
|
144 |
0.000065 |
0.000062 |
0.000061 |
0.000061 |
0.000061 |
0.000061 |
0.000043 |
41.86 % |
|
150 |
0.000043 |
0.000043 |
0.000043 |
0.000043 |
0.000043 |
0.000043 |
0.00 % |
|
Notes: In the analytical solution the deflections w in the center of the plate are determined according to the following formulas:
without taking into account the transverse shear deformations
\[ w=\frac{12\cdot \left( {1-\nu^{2}} \right)\cdot a^{4}\cdot p}{E\cdot h^{3}}\cdot \left[ {\frac{5}{384}-\sum\limits_{m=1}^\infty {\frac{\sin \left( {\frac{m\cdot \pi }{2}} \right)\cdot \left( {4+m\cdot \pi \cdot th\left( {\frac{m\cdot \pi }{2}} \right)} \right)}{m^{5}\cdot \pi^{5}\cdot ch\left( {\frac{m\cdot \pi }{2}} \right)}} } \right] \quad or \] \[ w=\frac{192\cdot \left( {1-\nu^{2}} \right)\cdot a^{4}\cdot p}{\pi ^{6}\cdot E\cdot h^{3}}\cdot \sum\limits_{m=1}^\infty {\sum\limits_{n=1}^\infty {\left[ {\frac{1}{m\cdot n}\cdot \frac{1}{^{\left( {m^{2}+n^{2}} \right)^{2}}}\cdot \sin \left( {\frac{m\cdot \pi }{2}} \right)\cdot \sin \left( {\frac{n\cdot \pi }{2}} \right)} \right]} } ; \] \[ At \quad \nu \quad = 0.2 w\approx 0.004062\cdot \frac{a^{4}\cdot p}{D}, \quad where: \quad D=\frac{E\cdot h^{3}}{12\cdot \left( {1-\nu^{2}} \right)}. \]
taking into account the transverse shear deformations
\[w=\frac{12\cdot \left( {1-\nu^{2}} \right)\cdot a^{4}\cdot p}{E\cdot h^{3}}\cdot \left[ {\frac{5}{384}-\sum\limits_{m=1}^\infty {\frac{\sin \left( {\frac{m\cdot \pi }{2}} \right)\cdot \left( {4+m\cdot \pi \cdot th\left( {\frac{m\cdot \pi }{2}} \right)} \right)}{m^{5}\cdot \pi^{5}\cdot ch\left( {\frac{m\cdot \pi }{2}} \right)}+\frac{8-3\cdot \nu }{10\cdot \left( {1-\nu } \right)}\cdot \left( {\frac{h}{a}} \right)^{2}} \cdot \left( {\frac{1}{32}-\sum\limits_{m=1}^\infty {\frac{\sin \left( {\frac{m\cdot \pi }{2}} \right)}{m^{3}\cdot \pi^{3}\cdot ch\left( {\frac{m\cdot \pi }{2}} \right)}} } \right)} \right] \quad or \] \[ w=\frac{192\cdot \left( {1-\nu^{2}} \right)\cdot a^{4}\cdot p}{\pi ^{6}\cdot E\cdot h^{3}}\cdot \sum\limits_{m=1}^\infty {\sum\limits_{n=1}^\infty {\left[ {\frac{1}{m\cdot n}\cdot \frac{1}{^{\left( {m^{2}+n^{2}} \right)^{2}}}\cdot \left[ {1+\frac{\pi^{2}\cdot h^{2}}{5\cdot \left( {1-\nu } \right)\cdot a^{2}}\cdot \left( {m^{2}+n^{2}} \right)} \right]\cdot \sin \left( {\frac{m\cdot \pi }{2}} \right)\cdot \sin \left( {\frac{n\cdot \pi }{2}} \right)} \right]} } ; \] \[ At \quad \nu \quad = 0.2 \quad w\approx 0.004062\cdot \frac{a^{4}\cdot p}{D}\cdot \left[ {1+4.533786\cdot \left( {\frac{h}{a}} \right)^{2}} \right], \quad where: \] \[ D=\frac{E\cdot h^{3}}{12\cdot \left( {1-\nu^{2}} \right)}. \]