Sectorial Properties of a C-shaped Thin-walled Section

Aim: To check the accuracy of the geometric properties calculation for a C-shaped thin-walled section.
Name of a file with the initial data: СSection.tns
Formulation: Check the accuracy of the geometric properties calculation for a thin-walled C-shaped rod cross-section.
References: Young W.C., Budynas R.G., Roark's Formulas for Stress and Strain, New York, McGraw-Hill, New York, 2002.
Initial data:
Geometric dimensions of a section:
b = 100 cm,
b1 = 30 cm,
h = 120 cm,
t = 3 cm.
Results Obtained in Tonus:
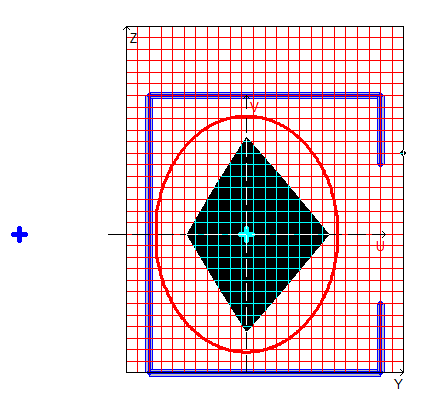
Design model, coordinate and principal axes, center of mass, ellipse of inertia, core of the section
Comparison of results:
|
Parameter |
Theory |
TONUS |
Deviation, % |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Cross-sectional area, A cm2 |
1140 |
1140 |
0 |
|
Conventional shear area along the principal U-axis, Av,y cm2 |
600 |
600 |
0 |
|
Conventional shear area along the principal V-axis, Av,z cm2 |
540 |
540 |
0 |
|
Torsional moment of inertia, It cm4 |
3420 |
3420 |
0 |
|
Sectorial moment of inertia, Iw cm6 |
8024714070,28 |
8024727272,72 |
0.00016 |
|
Y-coordinate of the shear center, yb cm |
-46,364 |
-46,364 |
0 |
|
Z-coordinate of the shear center, zb cm |
60 |
60 |
0 |
Sectorial Coordinate Diagrams
Notes: Geometric properties can be determined analytically by the following formulas:
\[ A=(2b+2b_{1} +h)t; \] \[ A_{v,y} =2bt; \] \[ A_{v,z} =t(h+2b_{1} ); \] \[ I_{t} =\frac{t^{3}}{3}\left( {h+2b+2b_{1} } \right); \] \[ e=b\frac{3h^{2}b+6h^{2}b_{1} -8b_{1}^{3} }{h^{3}+6h^{2}b+6h^{2}b_{1} +8b_{1}^{3} -12hb_{1}^{2} }; \] \[ I_{\omega } =t\left[ {\frac{h^{2}b^{2}}{2}\left( {b_{1} +\frac{b}{3}-e-\frac{2eb_{1} }{b}+\frac{2b_{1}^{2} }{h}} \right)+\frac{h^{2}e^{2}}{2}\left( {b+b_{1} +\frac{h}{6}-\frac{2b_{1}^{2} }{h}} \right)+\frac{2b_{1}^{3} }{3}(b+e)^{2}} \right]. \]